Yamaichi Electronic (Price Discovery)
Cautious Buy
Profile
A global leader in semiconductor test sockets, with an established overseas production and sales network.
Yamaichi Electronics Co., Ltd. was founded in 1956 and specialises in developing and manufacturing semiconductor test sockets and high-performance connectors. The company has a particular strength in sockets used in burn-in (high-temperature operation tests) and functional test processes for IC packages. It holds a leading position globally in this field. Its product portfolio is categorised into three major segments: (1) Test Solution Business (TS), (2) Connector Solution Business (CS), and (3) Optical Product Business (OPT). Among these, the TS segment has experienced sustained growth, supported by increasing demand from smartphones and data centres.
The revenue breakdown by segment is as follows: Test Solutions account for 43% (with an operating margin of 12%), Connector Solutions for 53% (5%), and Optical Products for 4% (-2%). By geography, overseas sales make up 87% of total revenue.
The company’s production and development bases span Japan (Sakura City, Chiba Prefecture), the Philippines, South Korea, and Germany. Additionally, it has established sales subsidiaries in key global markets to ensure a robust supply network. As of the end of FY03/2024, the company employed 2,123 people on a consolidated basis. Despite being a mid-sized company, Yamaichi possesses strong technological capabilities and precision processing skills that support high-value-added products and ensure strong profitability and growth potential.
| Securities Code |
| TYO:6941 |
| Market Capitalization |
| 50,907 million yen |
| Industry |
| Electronic equipment |
Stock Hunter’s View
Earnings have rebounded sharply on the recovery in demand for test sockets. Shareholder returns have surged; the following focal points are DRAM investment and progress on the medium-term plan.
Yamaichi Electronics focuses on test sockets used in semiconductor manufacturing processes and handles connectors and optical filters. In the previous fiscal year, earnings fell sharply, with operating profit dropping to just 30% of its prior level, due to a downturn in the semiconductor market, particularly in demand related to smartphones and PCs. However, in the current fiscal year, the company has achieved a V-shaped recovery back to record-high profit levels, driven by recovering demand for DRAM and ADAS-related applications. Notably, renewed investment in DRAM for generative AI applications has provided a strong tailwind.
Although the company’s performance is highly cyclical, its financial base remains sound, and it maintains double-digit ROE levels. It is also proactive in share buybacks, with annual repurchases exceeding 2.5 billion yen. The dividend was increased significantly to 89 yen, up from 31 yen in the previous year.
The share price is already trading at around 1.1x PBR, but the valuation does not appear excessively rich given the earnings recovery and high ROE. Going forward, investor focus is likely to turn to the execution of the medium-term plan and the timing of recovery in NAND-related demand.

Investor’s View
While market valuation remains cautious, the potential for earnings recovery suggests considerable upside. A modest position in portfolios is justifiable.
The company suffered from chronic losses and persistently low profitability until around a decade ago, but it succeeded in restructuring its operations. In recent years, it has restored and further strengthened its financial soundness. In the fiscal year ended March 2025, it captured the recovery in demand for smartphones and DRAM-related products in its Test Solution Business, resulting in a more than 180% increase in operating profit. ROE reached 12.2%, reflecting a notable improvement in capital efficiency, and progress in enhancing corporate value has been steady.
However, the company’s business is fundamentally cyclical, and its earnings are susceptible to fluctuations in capital investment trends, particularly in DRAM. Indeed, revenue and ROE have been volatile, contributing to the market’s cautious stance.
That said, the company has been highly proactive in its shareholder return policy, with share buybacks exceeding 2.5 billion yen last fiscal year and a substantial dividend increase. These capital policies support the stock’s valuation, which currently stands at a PBR of 1.11x and a PER of 9.0x.
Although the earnings yield is below 5%, and the stock may not appear particularly undervalued, applying a dividend model with a shareholder expected return of 8% implies that the current share price factors in an EPS growth rate of -18%, or -3% under the Gordon Growth Model. This suggests that the market is pricing the stock based on extremely conservative assumptions.
As such, if even minor signs of positive developments emerge—be it earnings surprises or progress in the medium-term plan—the stock may present meaningful upside. A modest position in portfolios may, therefore, be warranted.
Strong expertise and reliability in semiconductor sockets, with a globally entrenched position in niche markets.
Yamaichi Electronics’ main products are “burn-in sockets” and “test sockets” used in the inspection processes for IC chips. These are essential in ensuring the quality of semiconductor chips, which continue to advance in miniaturisation, high frequency, and high density and require exceptional reliability and precision in manufacturing. Backed by its capabilities in proprietary socket design and high-frequency-compatible probe pins, the company enjoys strong trust from numerous semiconductor manufacturers. The Test Solution Business (TS Business) forms the backbone of the company’s earnings.
The Connector Solution Business (CS Business) provides a wide range of high-performance connectors, mainly for communication equipment, automotive electronics, and industrial machinery. Demand for high-speed transmission solutions is rising, particularly in applications related to data centres and AI processing. The company also operates an Optical Product Business (OPT Business), which includes optical filters and laser light sources, although it accounts for less than 10% of total revenue.
One notable feature of the TS Business is that its earnings are highly dependent on the capital investment trends of its clients. However, because most of the products are customised for each client, switching costs are significant, and orders tend to be retained over time. In this way, the company has secured a robust position in high-value-added niche markets, which is a defining feature of its business.
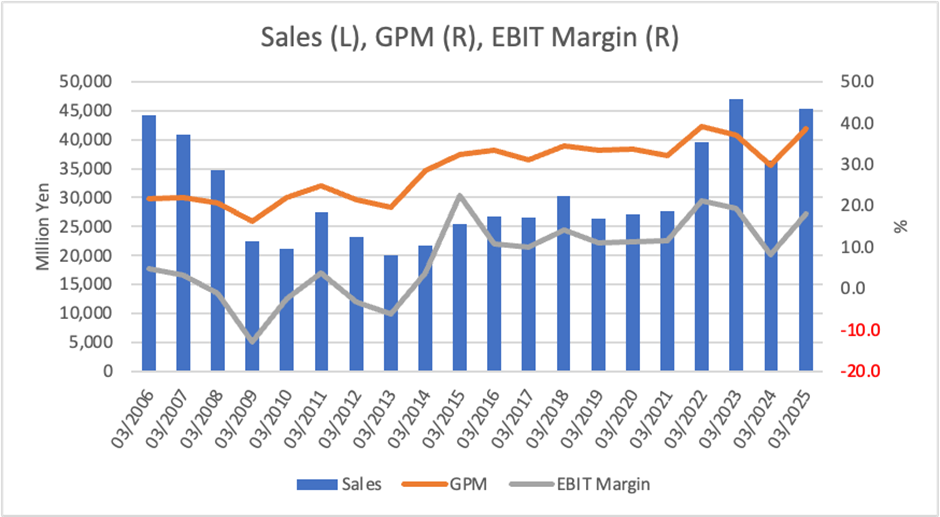
Although performance is subject to fluctuations in the semiconductor cycle, revenue and profit have shown a mid-term growth trend.
Yamaichi Electronics’ performance is characterised by a cyclical structure typical of the semiconductor industry, with substantial year-to-year volatility. However, from a mid- to long-term perspective, revenue increased from 27.6 billion yen in FY03/2021 to 45.3 billion yen in FY03/2025, representing a 64% gain over five years. Operating profit grew by approximately 2.6 times during the same period, indicating a notable improvement in profit margins.
This growth has been driven primarily by expanding the Test Solution Business (TS), particularly from rising demand for sockets used in DRAM and ADAS applications. The company’s ability to meet these high-precision and high-performance requirements has proven instrumental. In FY03/2025, the operating margin reached a high level of 18.2%, supported by disciplined cost control and improvements in production efficiency.
Conversely, the company’s performance has demonstrated sensitivity to cyclical peaks and troughs. In FY03/2024, for example, revenue declined from 46.9 billion yen to 36.4 billion yen, and operating profit fell sharply from 9.1 billion yen to 2.9 billion yen. This downturn stemmed from a rapid contraction in demand, especially in the smartphone and memory semiconductor segments, highlighting the high volatility in earnings as a key risk.
ROE has ranged between 5% and 23% in recent years, reaching a robust level of 12.2% in FY03/2025. Financial leverage remains low, with the equity ratio at 74.0%, underscoring the company’s solid financial foundation.
The Test Solution Business drove a substantial rebound, restoring earnings to record-high levels.
In the fiscal year ended March 2025, Yamaichi Electronics reported consolidated revenue of 45.2 billion yen, a 24.4% year-on-year increase, and operating profit of 8.2 billion yen, up 180.4%. The core Test Solution Business (TS) benefited from recovering demand for test sockets used in smartphones and PCs and renewed capital investment in DRAM for data centres. Segment revenue surged 59% year-on-year to 25.1 billion yen, and operating profit jumped 285% to 7.1 billion yen. Burn-in sockets for automotive ADAS performed exceptionally well, setting new sales records.
The Connector Solution Business (CS) saw revenue decline 1.5% year-on-year to 18.9 billion yen, as continued weakness in automotive and industrial applications—especially in Europe—offset growth in communications equipment. Operating profit rose 30% to 1.2 billion yen, aided by an increase in new products for data centre applications.
The Optical Product Business (OPT) remained under pressure, posting revenue of 1.2 billion yen (down 8.7% year-on-year) and an operating loss of 25 million yen, continuing its loss-making trend.
Operating cash flow improved significantly to 9.0 billion yen, and free cash flow reached 5.3 billion yen. With these gains, the company stepped up shareholder returns, executing share buybacks totalling over 2.5 billion yen during the fiscal year, the largest in its history.
Continued revenue and profit growth is planned for FY03/2026, with a clear commitment to achieving medium-term targets.
According to company forecasts, for the fiscal year ending March 2026, Yamaichi Electronics projects consolidated revenue of 47.4 billion yen (+4.6% YoY), operating profit of 8.5 billion yen (+3.3% YoY), ordinary profit of 7.9 billion yen, and net profit attributable to owners of the parent of 5.5 billion yen (+4.9% YoY). These figures are positioned as a stepping stone toward the final-year targets of the fourth medium-term management plan (FY03/2024–FY03/2026), which aim to exceed 50 billion yen in revenue and 10 billion yen in operating profit.
Demand for smartphone test sockets and DRAM for data centres in the Test Solution Business is expected to remain solid. However, recovery in demand for NAND-related and MCU-related products is projected to take longer. The first half of the fiscal year is thus forecast to be relatively subdued, with recovery momentum building toward the second half.
In the Connector Solution Business, demand for communication equipment is expected to grow, driven by continued investment in AI-related data centres. By contrast, the company remains cautious about recovery in the automotive and industrial machinery sectors.
The Optical Product Business is again forecast to have only a limited contribution this fiscal year.
Earnings per share (EPS) are forecast at 298.58 yen, a new record high. The current share price of 2,298 yen translates into an equity yield of approximately 13%, which significantly exceeds the company’s cost of capital. On this basis, the shares appear undervalued from a DCF perspective.
Expanding into next-generation device segments by strengthening ADAS-related offerings and responding to socket evolution. High cyclicality remains a structural risk.
Yamaichi Electronics’ growth strategy is centred on three pillars: (1) accelerating readiness for next-generation semiconductors, particularly in ADAS and AI applications, within its Test Solution Business; (2) strengthening global production capacity; and (3) making forward-looking investments in technological innovation. The TS Business, as the company’s main growth engine, is focused on product development for high-performance logic semiconductors, the transition to next-generation DRAM, and growing demand for automotive ADAS and autonomous driving systems.
The company operates in a sector where “reliability” and “precision” are paramount, especially in semiconductor testing. Its proprietary high-precision processing technologies and custom socket designs constitute competitive advantages that are not easily replicated. The high degree of product customisation per customer also results in substantial switching costs, leading to recurring orders over the long term.
However, the company’s biggest risk lies in its strong dependence on customers’ capital expenditure cycles—especially those of semiconductor manufacturers. In FY03/2024, for example, a sharp contraction in investment in smartphones and memory semiconductors resulted in a steep drop in both revenue and profit. The company’s earnings remain sensitive to changes in the external environment, including regional supply-demand dynamics (notably in China, North America, and Europe), geopolitical risks such as U.S.-China tensions, and global uncertainty.
In addition, slowing EV demand and prolonged inventory adjustment in Europe have negatively affected the CS business. For this segment to serve as a stable growth driver, the company must further diversify its product applications and optimise regional strategies.
Thus, while Yamaichi Electronics possesses specialised capabilities and strong earnings power, its cyclical business nature demands that investors closely monitor earnings catalysts and external developments.
Aiming for over 50 billion yen in sales and over 10 billion yen in operating profit in the final year, supported by expanded production capacity and strengthened technological capabilities.
Yamaichi Electronics is in the second year of its fourth medium-term management plan, covering FY03/2024 through FY03/2026. This plan centres on the commitment to “providing products and services that satisfy customers,” and sets final-year targets of over 50 billion yen in revenue and over 10 billion yen in operating profit. The company is simultaneously advancing both growth strategies and the reinforcement of its business foundation.
Key initiatives include: (1) serial development of next-generation socket products in the Test Solution Business, with applications for ADAS and data centre sectors; (2) reconstruction of its global production system, including the operation of the second building at the Sakura site and the third plant in the Philippines; and (3) structural reforms such as strengthening the domestic production framework and optimising the supply chain.
Progress to date shows that while the initial year of the plan (FY03/2024) saw revenue of 36.4 billion yen (94% of target) and operating profit of 2.9 billion yen (29% of target), the second year (FY03/2025) improved substantially with 45.2 billion yen in revenue and 8.2 billion yen in operating profit—putting the company back on a realistic trajectory to meet its final-year goals. The growth of the TS Business has been particularly instrumental in this turnaround.
Financially, the company is targeting ROE above 10%, a dividend payout ratio of 30%, and a total shareholder return ratio above 40%. In FY03/2025, it delivered on these goals with ROE of 12.2%, a payout ratio of 34.3%, and significant buybacks as part of an aggressive shareholder return strategy.
Planned cumulative capital expenditures for FY03/2024–FY03/2026 total 14 billion yen, marking a pace over 30% higher than historical levels. This signals an evident willingness to invest in long-term growth while maintaining capital efficiency.
Share Price Trends and Valuation
Despite a sharp earnings recovery, the stock trades at conservative valuation multiples. There is room for upward revision.
In FY03/2025, Yamaichi Electronics posted record-high earnings, yet the stock remains conservatively valued with a forward PER of 9.0x and a PBR of 1.11x. This suggests the market continues to take a cautious view on the sustainability of the company’s performance, particularly in light of the cyclical nature of semiconductor-related capital investment.
Earnings per share (EPS) reached 259.47 yen and book value per share (BPS) stood at 2,037.62 yen—both at record levels. ROE was also high at 12.2%. Despite this, the single-digit PER indicates that investors treat this profit level as potentially transient.
Looking ahead to FY03/2026, the company forecasts EPS of 298.58 yen. The current share price of 2,298 yen implies an equity yield of approximately 13%, well above the company’s cost of capital. The stock is undervalued from a discounted cash flow (DCF) perspective.
Furthermore, the company repurchased over 2.5 billion yen of shares in FY03/2025 and is on track to exceed a 40% total shareholder return ratio. Continued execution of shareholder-friendly capital policies will likely support a stock re-rating.
In conclusion, the current valuation reflects overly conservative assumptions regarding future earnings. Should any positive surprises emerge—such as stronger-than-expected earnings or acceleration in medium-term plan execution—there may be significant upside potential.
In addition to stable trust bank holdings, foreign institutional investors and activist funds maintain significant stakes.
According to the securities report as of March 2024, the largest shareholder is Custody Bank of Japan, with 3.2 million shares (15.65% of the total). The second largest is The Master Trust Bank of Japan, holding 2.8 million shares (13.70%). These two trust banks account for roughly 29% of the company’s issued shares, establishing a stable shareholder base.
At the same time, several foreign funds—including NIPPON ACTIVE VALUE FUND (4.82%), RE FUND 107-CLIENT AC (3.91%), STATE STREET BANK (2.81%), and BNP PARIBAS LUXEMBOURG (1.95%)—also maintain meaningful stakes, indicating the presence of active institutional interest.
As of the end of March 2025, the company held 1,386,398 shares of treasury stock, representing approximately 6.35% of issued shares. This contributes to improving both dividend payout and total shareholder return ratios. Additionally, the employee stock ownership plan holds 1.61%, reflecting an internal alignment of interests in corporate value creation.
By category, foreign investors collectively held 35.8% of total shares, suggesting that global investors are paying attention to the company’s valuation and governance.
Financials and Valuations

Price

PBR (LTM)

PER (LTM)

ROE (LTM)

EPS (LTM)

Dividend Yield (LTM)

