Rasa Industries (Price Discovery)
Buy on Weakness
Profile
Rasa Industries is a chemical manufacturer that specializes in producing high-purity phosphoric acid for the semiconductor industry, while also handling coagulants, electronic materials, and equipment used in construction and civil engineering. Established in 1918. The core Chemicals segment accounts for over 80% of total revenue, featuring a diversified structure that includes Machinery and Electronic Materials.
The company’s segment sales composition (operating profit margin) is as follows: Chemicals, 84% (13%); Machinery, 10% (3%); Electronic Materials, 4% (16%); Others, 2% (64%). The overseas sales ratio has reached 41%, and production bases are located in Japan, Taiwan, and South Korea. Production in the United States is scheduled to begin in 2027, establishing a globally stable supply system (all figures as of FY3/2025).
| Securities Code |
| TYO:4022 |
| Market Capitalization |
| 32,134 million yen |
| Industry |
| Chemistry |
Stock Hunter’s View
Strong performance in phosphoric acid for semiconductors. The AI boom serves as a powerful tailwind.
Rasa Industries holds a domestic share of over 50% in high-purity phosphoric acid, which is indispensable for semiconductor manufacturing. It is produced in three countries—Japan and Taiwan through consolidated subsidiaries, and South Korea through an equity-method joint venture—and conducts local production and local sales to semiconductor-related users in each country. A new joint venture plant is scheduled to begin operations in the United States in 2027, establishing a four-country production system.
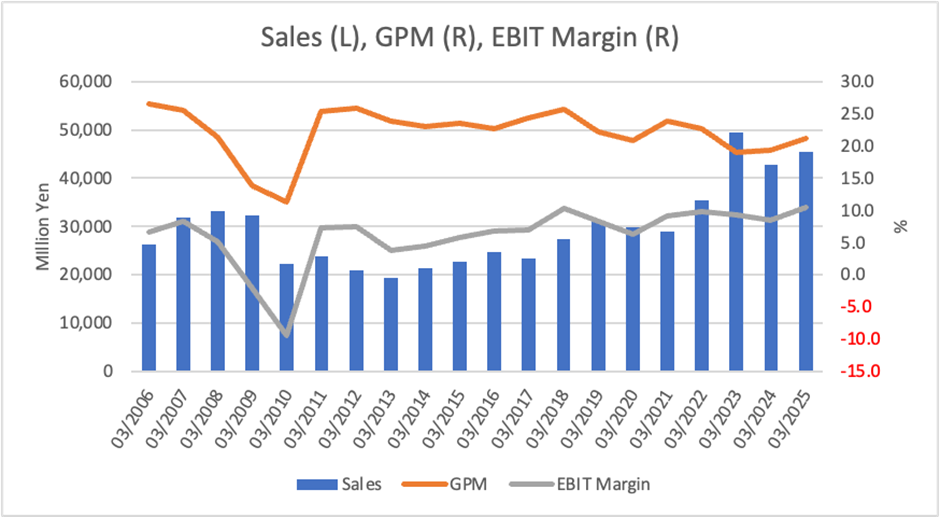
Sales of high-purity phosphoric acid for AI semiconductor production are growing. In the fiscal year ended March 2025, profits at each stage increased by more than 30%, with operating profit reaching a record high. The semiconductor market continues to recover, and for the current fiscal year, the company plans sales of 49.2 billion yen (an 8.3% YoY increase) and operating profit of 5.1 billion yen (a 7.7% YoY increase).
Meanwhile, the “Medium-Term Management Plan 2026” sets targets of 52.0 billion yen in sales, 4.8 billion yen in operating profit, and ROE of 10% for the fiscal year ending March 2027. Still, the operating profit target has already been virtually achieved two years ahead of schedule. The forecast for the fiscal year ending March 2026 also gives a conservative impression, and it is expected that the outlook will be revised upward in due course.
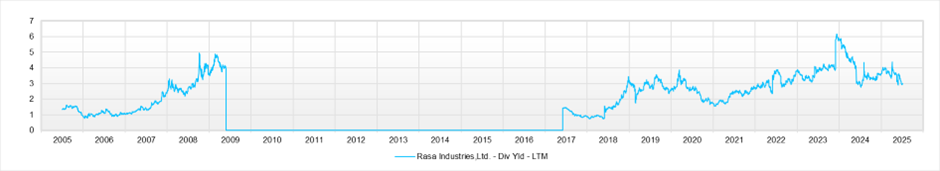
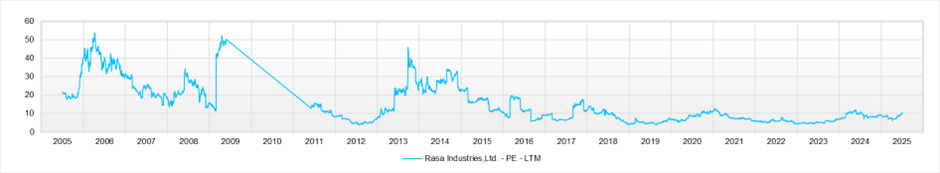
The core Chemicals segment includes, in addition to high-purity phosphoric acid, coagulants for etching electronic components and materials for capacitors, with the overall growth of the high-tech sector serving as a tailwind. The annual dividend for the current fiscal year is 128 yen, and the dividend yield remains in the attractive 3% range. The current PER is below 10x, and the PBR is slightly above 1x, leaving room for further upward revaluation.
Investor’s View
Buy on Weakness. Despite stable ROE and steady growth, the market remains cautious. The equity yield remains attractive.
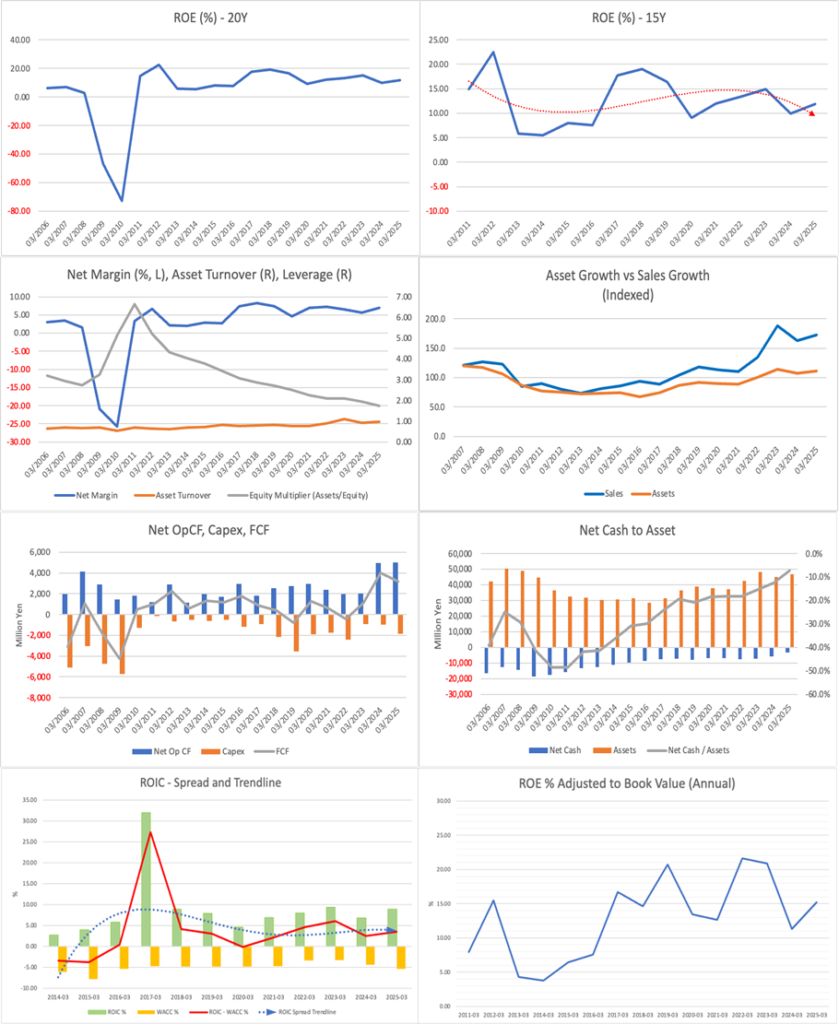
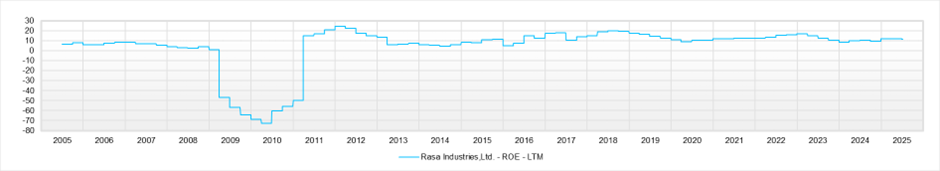
The company is a semiconductor-related stock, but its business shows generally stable top-line growth, and earnings volatility is limited. ROE has remained within the range of 10–15%, supported by the stability of net profit margins. The spread between ROIC and WACC is around 4%, which is ordinary, but capital efficiency has consistently remained in positive territory.
The sharp increase in cash flow over the past two years is noteworthy. Even as sales have surged due to the expanding demand for AI semiconductors, profit margins have been maintained, indicating the strength of the business structure.
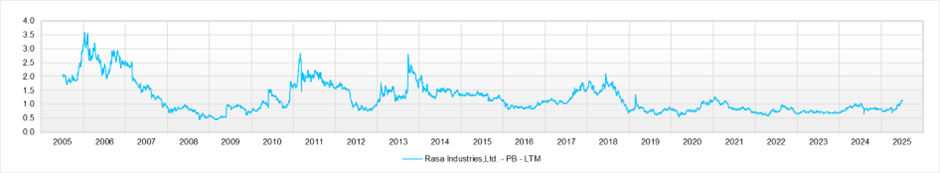
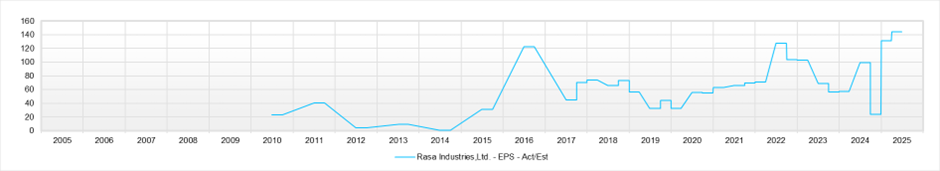
PBR is 1.13x, forecast PER is 9.71x, forecast ROE is 11.8%, and the payout ratio is 30%, so the implied EPS growth rate is limited to +0.2%. In fact, the EPS CAGR over the past five years is +18%, a high level, and based on long-term performance as well, the company is not a cyclical business. The market’s valuation appears excessively cautious. The equity yield exceeds 10%.
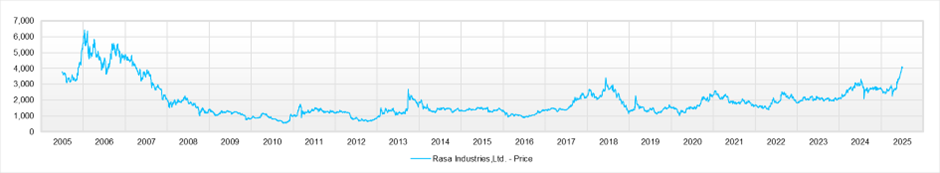
On the other hand, financial leverage has declined significantly, thereby suppressing further improvement in ROE. Share buybacks are a strong option for improving capital efficiency. The stock price has risen 50% since May, and the current level appears to be overheated. It is desirable to accumulate the stock on dips for short- to medium-term portfolios.
Recent Financial Results
Led by the Chemicals segment amid a recovery in semiconductor demand, each profit level increased by over 30%. Operating profit reached a record high.
In the fiscal year ended March 2025, net sales were 45.4 billion yen (up 6.2% YoY), operating profit was 4.7 billion yen (up 31.9%), and ordinary profit was 4.6 billion yen (up 35.5%). Net profit attributable to owners of parent was 3.1 billion yen (up 31.4%), resulting in significant profit increases of over 30% at each level.
The primary factor driving profit growth was the increase in sales volume of high-purity phosphoric acid for semiconductors in the Chemicals segment, which was supported by a recovery in market conditions. On the other hand, the Machinery segment reported a decline in profit due to reactionary decreases in plant sales and inventory valuation losses. The Electronic Materials segment also experienced a decrease in profit, primarily due to lower sales. By segment, only the Chemicals segment showed a profit increase, with a significant rise of +59.9% compared to the same period of the previous year.
Operating cash flow was slightly higher than the previous year at 5.0 billion yen, maintaining a steady profit-generating capacity. Financial cash flow was a negative 1.6 billion yen due to debt repayments and other factors. Still, the cash and equivalents balance at the end of the period increased to 5.0 billion yen from the previous year.
Full-Year Forecast
For the fiscal year ending March 2026, revenue and profit are expected to continue increasing. The dividend will also be increased to 128 yen.
According to the company’s plan, for the fiscal year ending March 2026, net sales are projected at 49.2 billion yen (up 8.3% YoY), operating profit at 5.1 billion yen (up 7.7%), ordinary profit at 4.9 billion yen (up 6.5%), and net profit at 3.3 billion yen (up 5.4%), indicating continued growth in both revenue and profit.
By segment, the Chemicals business is expected to record 42.0 billion yen in sales (+10.0%), the Machinery business 4.5 billion yen (+0.2%), and the Electronic Materials business 1.6 billion yen (+1.6%), with all segments showing a slight upward trend in sales.
The dividend is planned at 64 yen for the interim and 64 yen for the year-end, totaling 128 yen annually—an increase of 8 yen compared to the previous fiscal year. The assumed exchange rate is 145 yen per USD, which may serve as a tailwind in the current yen depreciation environment.
Growth Strategy and Risks
Strengthening overseas expansion of the Chemicals segment and deepening dependence on semiconductors. The U.S. plant holds the key.
The company’s growth strategy is based on “Rasa Vision 2033” and the Medium-Term Management Plan 2026, with the following three points as its main pillars:
Global expansion of high-purity phosphoric acid:
Following Taiwan, a production base will also be established in the United States to strengthen the supply system in regions with strong semiconductor demand. The company aims to respond precisely to demand for AI semiconductors and advanced logic applications.
Capital efficiency management focused on ROIC:
Rather than focusing on operating profit targets, ROE of 10% and maintaining ROIC are set as core indicators. The company will promote selection and concentration in its revenue structure.
Sustainability initiatives:
The company aims to build a low-impact portfolio through the development of coagulants for water treatment and deodorization, as well as adsorbents for radioactive iodine.
Risk factors include:
① Sudden changes in the semiconductor market conditions,
② Sharp increases in raw material prices (such as phosphate rock),
③ Delays in the start-up or cost overruns of new plant operations,
④ Decline in profitability in the Machinery segment.
Medium-Term Management Plan
The numerical targets have already reached achievement levels. The focus is now on upward revisions of the outlook.
The Medium-Term Management Plan “2026” sets targets of 52.0 billion yen in sales, 4.8 billion yen in operating profit, and ROE of 10% or higher for the fiscal year ending March 2027. However, as of the fiscal year ended March 2025, the company had already achieved 4.7 billion yen in operating profit, and the current forecast stands at 5.1 billion yen—virtually clearing the numerical targets two years ahead of schedule.
This plan advocates management that is conscious of capital costs, balancing growth investment and returns, and accelerating globalization. In particular, the operation of the joint-venture U.S. plant is a milestone that represents substantive progress in the mid-term plan.
For this reason, there is a possibility that earnings forecasts and the mid-term plan itself will be revised upward during the fiscal year ending March 2026, making it likely to attract attention from the capital market.
Stock Price and Valuation
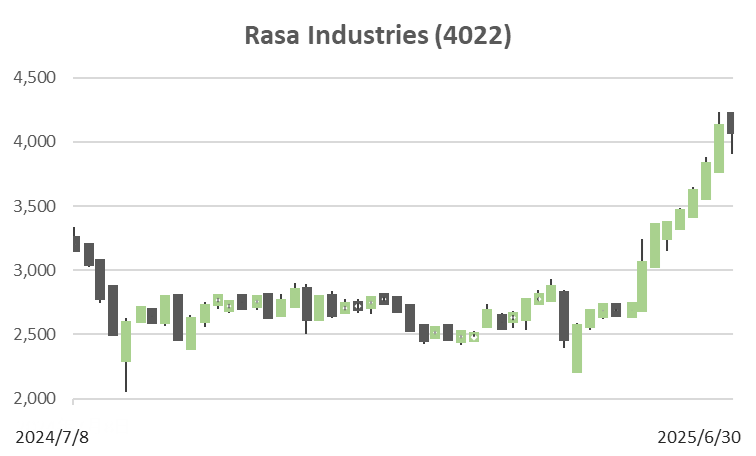
Since May, the stock price has surged over 50%. However, the equity yield remains above 10%, and growth expectations have not yet been fully priced in.
The stock price surged after May 2025, recording an increase of more than 50% in a short period. However, even at the current price level, the valuation does not appear excessive.
The forecast PER is 9.71x, PBR is 1.13x, and forecast ROE is 11.8%. Based on these figures, the implied EPS growth rate is only +0.2%. In reality, the EPS CAGR over the past five years is +18%, but the market has barely priced in the company’s future growth potential.
The payout ratio is 30%, and the dividend yield is in the upper 3% range. The equity yield exceeds 10%. The gap between capital efficiency and the market’s evaluation remains large, and the valuation is excessively cautious given the stability of the ROE.
If concrete milestones such as the early achievement of mid-term numerical targets and the launch of the new U.S. plant become visible, the potential for revaluation going forward appears significant.
Shareholder Structure
Founding-related holdings and major customer companies are among the top shareholders. The free float ratio is high, and attention should be paid to price movements from a supply-demand perspective.
As of the fiscal year ended March 2025, the major shareholders are as follows:
- Rasa Industries Business Cooperation Association: 5.45%
- RS Technologies: 4.66% (major customer)
- Sumitomo Mitsui DS Asset Management: 5.00%
- Asset Management One: 3.61%
- Mizuho Financial Group: 3.15%
- Other domestic institutional investors, such as Nomura Asset Management and Mitsubishi UFJ Asset Management, also hold shares in dispersed amounts just below 3%.
The top 10 shareholders account for approximately 35% in total, with about 10% held by business affiliates and major customers, and about 25% by financial institutions and asset management firms. The company has approximately 1.7% of its shares.
The fact that the top shareholder is the Business Cooperation Association indicates the company’s nature as a publicly held firm without family ownership, while also making it a structure that can attract investor interest depending on its IR and capital policies.
The free float ratio is generally over 70%, and caution is warranted regarding short-term stock price volatility due to rapid changes in supply-demand dynamics or theme-driven trading.
Financials and Valuations
Price
PBR (LTM)
PER (LTM)
ROE (LTM)
EPS (LTM)
Dividend Yield (LTM)