Nippon Soda (Price Discovery)
Weak Hold
Conclusion
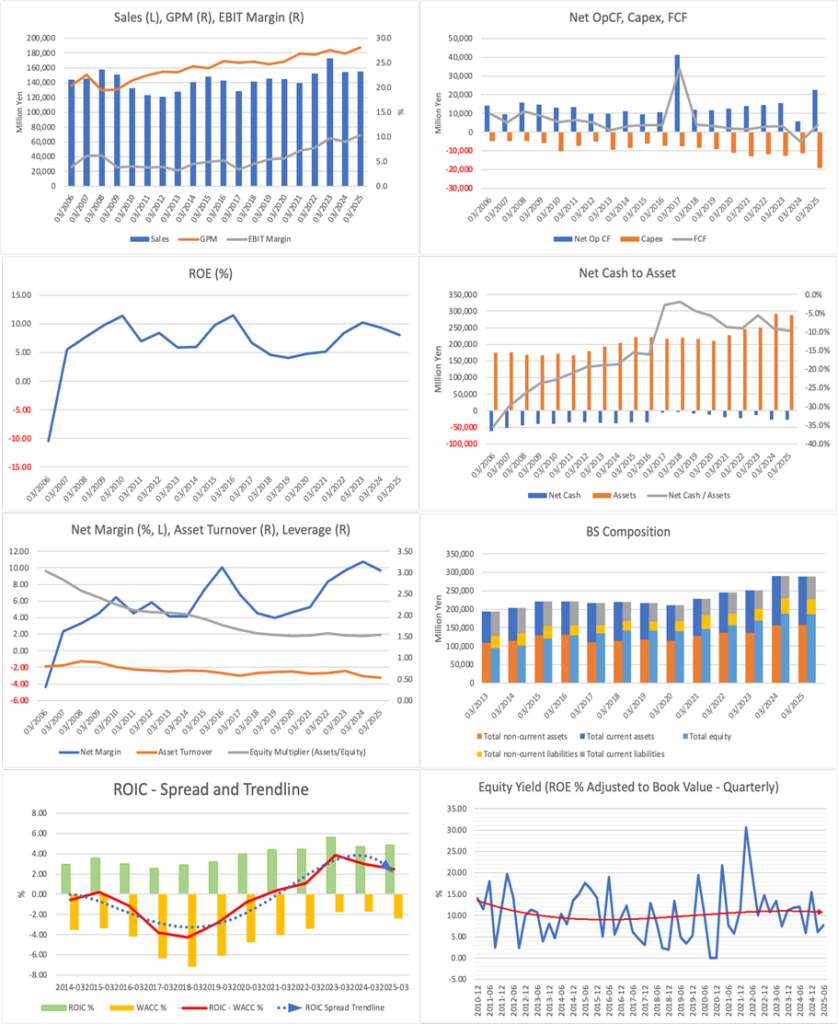
Weak hold. The fair value range is estimated to be 3,700–4,300 yen (The median of the blended distribution of the three methods is 3,800 yen). The current valuation implies an EPS growth of approximately 3% per annum. Given that EPS has been flat over the last 3–4 years, the upside appeal of the current share price is limited. While we acknowledge margin improvement since 2018 and steady top-line growth, free cash flow remains structurally thin due to the necessity to spend on capital expenditure. Bringing forward achievement of 10% ROE and strengthening total shareholder returns are re-rating triggers.
Profile
A composite portfolio spanning Chemical Materials / Agribusiness / Trading & Logistics, etc.
The company is a chemical manufacturer with businesses in Chemical Materials, Agribusiness, Trading & Logistics, Engineering, and Eco-Solution. In the first quarter of FY3/2026, normalising inventories in Agribusiness and higher sales in Chemicals and Trading contributed, as noted above. The year started with higher sales and profits. Sales mix by segment % (operating margin %): Chemical Materials 23 (12), Agribusiness 35 (10), Trade & Logistics 28 (5), Engineering 8 (11), Eco-Solution 6 (1) <FY3/2025>
| Securities Code |
| TYO:3386 |
| Market Capitalization |
| 198,473 million yen |
| Industry |
| Chemistry |
Stock Hunter’s View
Holds many niche proprietary products. From FY3/2027 onward, earnings growth will accelerate.
Nippon Soda is a long-established chemical manufacturer with over 100 years of history, centered on agricultural chemicals. The “Agribusiness” segment—whose mainstays are fungicides and insecticides/acaricides—and the “Chemical Materials” segment—handling pharmaceutical excipients, caustic soda, etc.—are the earnings pillars. After five years of shedding unprofitable businesses, the company is about to enter a phase of earnings expansion.
In Chemical Materials, sales are increasing for the resin additive “NISSO-PB” for copper-clad laminates used in AI servers and for the pharmaceutical excipient “NISSO HPC”; in Agribusiness, exports are growing for the fungicides “Picarol” and “Pancho,” and the acaricide “Nissorun.” Among these, HPC is operating at full capacity on strong customer demand, and high growth is expected from the first half of FY3/2027 onward, when new capacity comes online. Production capacity will be increased to 1.5× the current level. Until then, growth in shipment volumes will be limited; however, the company will seek to improve profitability by expanding sales of higher-value-added grades.
Additionally, inventory adjustments in Agribusiness are almost complete. The company will expand sales of three new agrochemicals. This segment has a 70% overseas sales ratio and is particularly strong in Europe. Over the medium to long term, based on technologies developed in pesticide research, the company plans to focus on animal health as a new business, and the upcoming development progress warrants close attention.
Investor’s View
Weak hold. A logical but time-consuming share-price re-rating. A thick base of hard assets underpins earnings, but as a trade-off, FCF is thin.
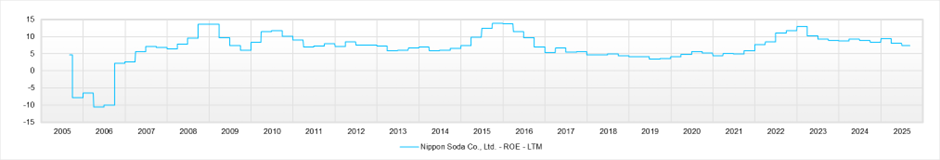
The current investment stance is neutral. Combining three methods—the PBR method, a multi-stage DDM, and DCF (FCFF)—we estimate a fair value range of 3,700–4,300 yen (median 3,800 yen). While management’s capital-efficiency target of “ROE 10% in FY3/2030” and steady business progress are encouraging, there is little clear undervaluation versus the current share price.
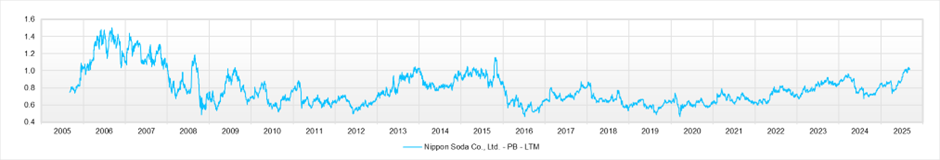
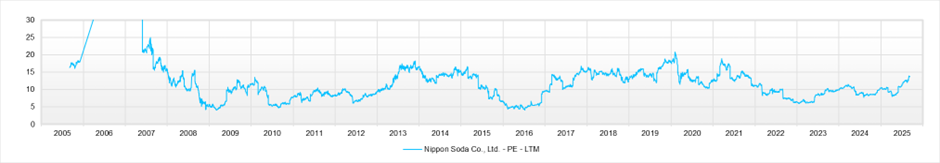
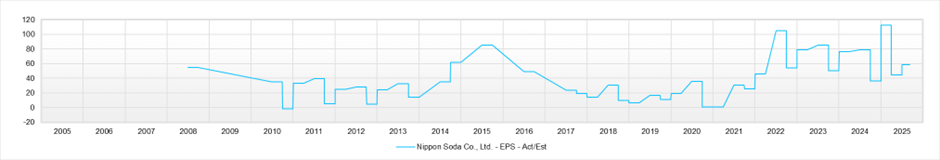
Moreover, under the EPS growth of around 3% per year implied by the current metrics—forecast PER 14.0 / actual PBR 1.01 / forecast ROE 7.4% (with EPS broadly flat over the last 3–4 years)—we judge that near-term valuation appeal is not large. Absent a near-term positive surprise in EPS, the investment stance remains neutral.
Upside scenarios for fair value are (i) bringing forward achievement of 10% ROE, (ii) strengthening total shareholder returns through dividends plus share repurchases, and (iii) growth in semiconductors and functional materials and an improved price mix. Downside factors include intensifying generic competition in Agribusiness and cases where FCFF does not increase due to investment and working capital growth beyond assumptions.
The medium-term management plan is consistent, but assessing execution capability remains an issue.
The path of gradual improvement from ROE 8% to 10% over five years may appear uninspiring at first glance. Still, it can also be evaluated as a logical medium-term program that balances growth with improvement in returns on capital. However, the plan is full of positives, and assessing execution capability remains an issue. In the first quarter of FY3/2026, net sales totaled 32.639 billion yen (up 1.4% year-over-year) and operating income reached 3.156 billion yen (up 2.8% year-over-year), marking a strong start to the year with higher sales and profits.
Steady top-line growth and continued margin improvement since 2018. FCF is hard to generate because it is an asset-intensive model.
The company’s fundamental appeal lies in maintaining steady top-line growth over the long term while sustaining higher margins since 2018. Additionally, cash flow generation has also expanded. On the other hand, the company is a typical capital-intensive business, and because much of its operating cash flow is reinvested in capital expenditures, generating free cash flow is a complex process. As of the end of June 2025, fixed assets totaled approximately 163.8 billion yen, and total assets were approximately 289.7 billion yen, resulting in a fixed-asset ratio of roughly 56%, indicating a high asset intensity. This substantial asset base serves as the foundation for sustained supply capacity and competitiveness; however, in exchange, FCF is relatively thin.
Management plan: expanding growth drivers and creating new businesses, optimizing capital allocation, and improving the quality of total returns.
The management plan is structured to expand growth-driver products further, while also creating new businesses, such as OLED and animal health. In capital allocation, the company expects to allocate 30.0 billion yen for growth investments and 40.0 billion yen for R&D, and will steadily advance balance-sheet reform by reducing inventories and unwinding cross-shareholdings. Furthermore, by flexibly raising interest-bearing debt, the company aims to increase financial leverage and optimize the capital structure. Regarding shareholder returns, by introducing a progressive dividend policy and flexibly executing share repurchases, the company clearly demonstrates its commitment to enhancing the quality and sustainability of total returns. In fact, at the Board meeting dated May 14, 2025, the company resolved share repurchases of up to 2.5 million shares / 5.0 billion yen, with the acquisition period from May 15, 2025, to January 31, 2026; progress as of August 31, 2025, was 692,600 shares, approximately 2.19 billion yen.
Financials and valuations
Price
PBR (LTM)
PER (LTM)
ROE (LTM)
EPS (LTM)
Dividend Yield (LTM)