Kidswell Bio (Company Note – 1Q update)

| Share price (8/15) | ¥232 | Dividend Yield (23/3 CE) | – % |
| 52weeks high/low | ¥864 / 229 | ROE(TTM) | -32.17 % |
| Avg Vol (3 month) | 273.2 thou shrs | Operating margin (TTM) | -58.57 % |
| Market Cap | ¥7.3 bn | Beta (5Y Monthly) | 1.15 |
| Enterprise Value | ¥7.0 bn | Shares Outstanding | 31.444 mn shrs |
| PER (23/3 CE) | – X | Listed market | TSE Growth |
| PBR (22/3 act) | 4.37 X |
| Click here for the PDF version of this page |
| PDF Version |
SHED and MCB are in the final stages.
GBS-007 shipped smoothly and contributed to earnings.
◇Summary of 1Q results for FY2023/3
In 1Q FY2023/3, Kidswell Bio’s cell therapy business (regenerative medicine) for SHED (Stem cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous teeth) progressed steadily, while MCB (Master Cell Bank) development was in the final stage. The biosimilar (BS) business, a source of income for the foreseeable future, made a significant contribution to sales, with the third product, ranibizumab BS (GBS-007), performing well. As a result, sales in 1Q FY2023/3 were 610 million yen (vs consolidated sales of 303 million yen in the same period of last fiscal year), and operating loss was 37 million yen (vs operating loss of 309 million yen in 1Q of FY2022/3).
◇A view on share price
The company’s share price hit a limit-low on the FY2022/3 result announcement, which included the its strategic decision to postpone the return to profitability expected in FY2023/3. The share price has been declining ever since, and the shares’ PBR is well below the past three year average of 9.24. Investors appear to be struggling to evaluate the new growth story. On the other hand, the 1Q results revealed better-than-expected sales of GBS-007, which made it highly likely that the company will achieve its full-year forecasts. In addition, if positive news is announced in the future, such as the completion of MCB and the identification of concrete development and progress in several SHED development projects, there should emerge signs of a share price turnaround.
◇Results for 1Q FY2023/3
The company posted sales of 601 million yen, an operating loss of 37 million yen and a net loss of 80 million yen in the quarter. In April 2022, the company transferred its consolidated subsidiary Japan Regenerative Medicine Co., Ltd. to Metcela Inc., and will therefore announce non-consolidated financial results from this financial year. Although an apple-to-apple YoY comparison will not be possible, sales and profits have made significant progress and improved well.
In terms of sales, GBS-007, the third BS product, received more orders than expected after its launch in December 2021, contributing significantly to sales growth. Sales of existing BS, GBS-001 and GBS-011 also remained strong.
The overall gross margin has declined. While the cost reduction effect of GBS-001 continues to contribute, the effect of the cost reduction measures for GBS-007, whose sales are growing, has not kicked in (however, the figures for the same period of the last year are on a consolidated basis and are therefore for reference only). R&D and other SG&A expenses in SG&A expenses were in line with initial plans. As the costs of manufacturing MCB and GBS-007 were not incurred until 2Q, the expenses recorded in 1Q were limited, resulting in an operating loss of 37 million yen, which was significantly lower YoY (a loss of 309 million yen in the same quarter of last fiscal year on a consolidated basis). Also, the net loss for the quarter contracted, posting 80 million yen, down from 314 million yen a year earlier.
| JPY, mn, % | Net sales | YoY % |
Oper. profit |
YoY % |
Ord. profit |
YoY % |
Profit ATOP |
YoY % |
EPS (¥) |
| 2019/3 | 1,021 | -3.6 | -805 | – | -816 | – | -856 | – | -43.84 |
| 2020/3 | 1,077 | – | -1,161 | – | -1,187 | – | -7,316 | – | -264.65 |
| 2021/3 | 996 | -7.5 | -969 | – | -991 | – | -1,001 | – | -34.79 |
| 2022/3 | 1,569 | 57.7 | -919 | – | -952 | – | -535 | – | -17.35 |
| 2023/3 (CE) | 2,900 | – | -980 | – | -999 | – | -1,000 | – | -31.82 |
| 2022/3 1Q* | 303 | 150.1 | -309 | – | -313 | – | -314 | – | -10.50 |
| 2023/3 1Q | 610 | – | -37 | – | -80 | – | -80 | – | -2.57 |
* Figures through FY2022/3 are on a consolidated basis. Figures for 1Q FY2023/3 and thereafter are on a non-consolidated basis, and year-on-year comparisons are not shown. Figures for 1Q FY2022/3 are on a consolidated basis and are for reference only.
In BS, as previously reported, a bank loan of 1 billion yen was booked at the end of June to finance working capital for the increase in sales of GBS-007. As a result, cash and deposits at the end of 1Q stood at 1.53 billion yen. Total assets amounted to 4.30 billion yen, increasing by 0.83 billion yen from the end of FY2022/3.
As a subsequent event, the company received approximately 500 million yen on 14 July through equity finance described below, which included the issuance of the 4th convertible bond with stock acquisition rights, etc.
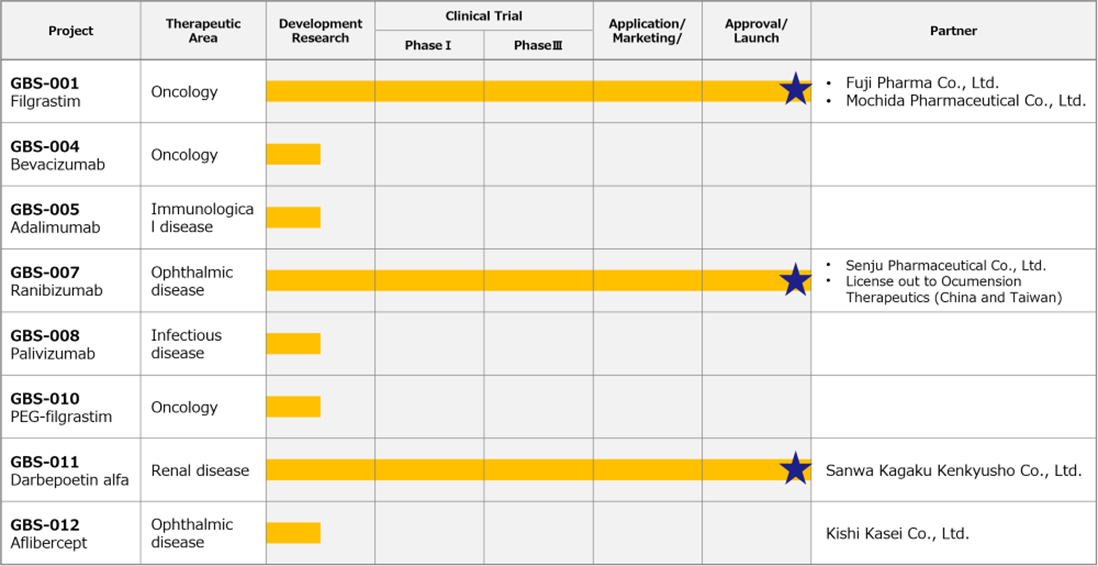
◇Biosimilars business: sales of GBS-007 were stronger than expected.
*Ranibizumab (GBS-007): The third product in the BS business, ranibizumab BS, an anti-VEGF antibody drug for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration, was launched on 9 December 2021 by Senju Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., the company’s development partner. As the first BS in the ophthalmology field, this has attracted a lot of attention and sales have been strong, with orders exceeding initial forecasts. The company will use the fundraising described below to increase production.
*Filgrastim (GBS-001): It is a BS that a partner has already launched. GBS-001 has also undergone cost-cutting measures, and profitability has been improved. It is reported that Mochida Pharmaceutical has decided to discontinue sales of GBS-001, but this will not affect the company’s forecasts for the current financial year and its medium-term strategic plan.
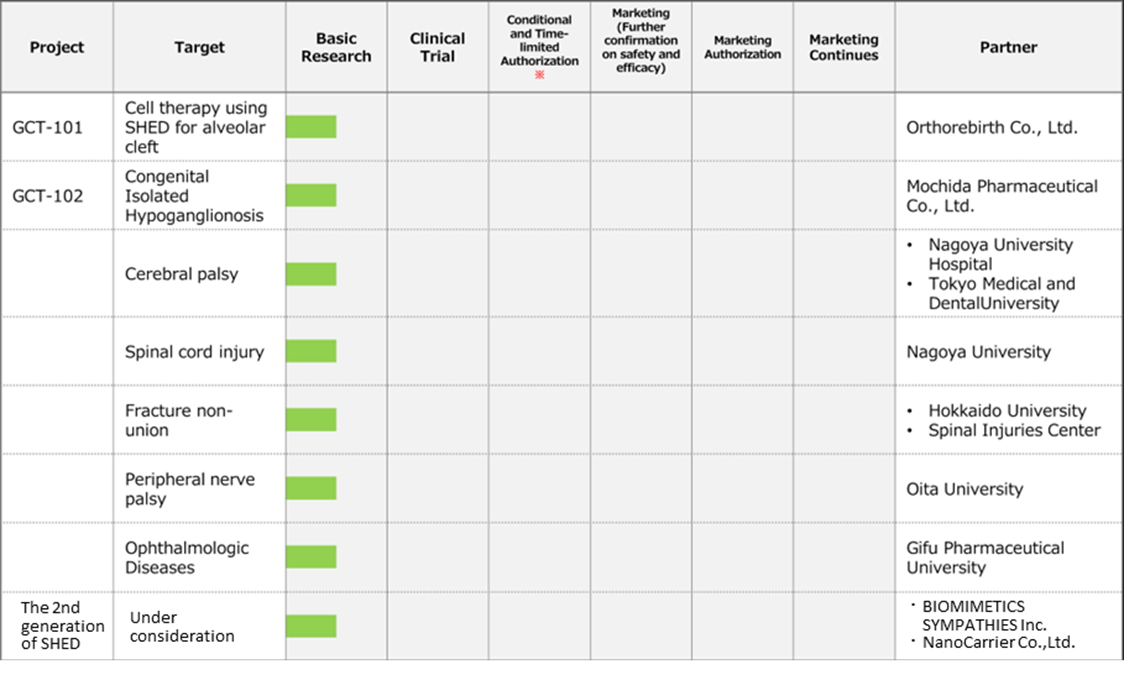
◇Cell therapy business (regenerative medicine): MCB development is in the final stage.
*Completion of Master Cell Bank (MCB): Establishing a stable supply system for the raw materials needed for research and development is essential in advancing the SHED business. The company is working with ChiVo Net to recruit donors to produce the raw material, has formed alliances with university hospitals, and is building an MCB supply structure with Nikon CeLL innovation Co., Ltd. The company started GMP manufacturing in October 2021, which is necessary to supply MCBs as raw materials. It is currently conducting the final quality inspection tests of MCBs and is close to completion of MCB. Sales and costs associated with the completion of MCB are expected to be recorded from 2Q onwards.
◇ New biologics business : the company signed a joint research agreement with Chiome Bioscience.
*Joint research with Chiome Bioscience: The company positions the new biologics business as part of its key future growth strategy. However, as the development of bio-new drugs requires a vast amount of research resources, joint research with other companies that are strong in their respective fields of expertise is effective. Chiome Bioscience (TYO: 4583) is engaged in the antibody drug discovery business and drug discovery support business. It possesses various technologies, systems and know-how required for developing antibody drugs. The company has a pipeline of more than a dozen products, including out-licensed products, in-house developed products and out-license candidates, and an oncology antibody drug (CBA-1205) is currently undergoing clinical trials. Kidswell Bio aims to accelerate the research activities of its development candidates by combining the two companies’ management resources, knowledge and technologies, mainly in the field of antibody drug development in the bio new drug business.
◇ Financing in response to increased orders for GBS-007
The company raised funds in response to an increase in orders for drug substance and formulations of GBS-007, and to bolster facilities for the manufacturing and sales system aiming at long-term stable supply. The company’s BS business model specialises in BS research and development, as the company relies on CMOs to provide the products for pharmaceutical companies. As a result, the company needs to secure working capital to meet orders from pharmaceutical companies and incur orders and prepayment costs to CMOs.
In June, the company announced that it would raise a total of 1.9 billion yen through long-term borrowing from banks (1 billion yen) and equity finance (500 million yen convertible bonds and 400 million yen stock acquisition rights) to meet the increased orders for GBS-007.
Although a bank loan of 1 billion yen is a substantial amount, it means a recognition of GBS-007’s solid profitability in the future. With the combination of debt and equity, the company takes into account the stability of financial discipline.
According to the company, bank loans are mainly used for working capital. The equity financing is planned to be used to fund the expansion of manufacturing capacity to strengthen the stable supply structure over the medium to long term in response to the increasing orders for GBS-007.
(For more information, see https://www.kidswellbio.com/Portals/0/resources/pdf/en/20220623_Press%20Release_%E6%8E%B2%E8%BC%89%E7%94%A8.pdf?TabModule605=0)
◇ Forecast for FY2023/3
The forecasts of net sales of 2.9 billion yen, operating loss of 0.98 billion yen and net loss of 1.0 billion yen are unchanged from the initial forecasts. As of 1Q, sales are running slightly behind the full year estimate. The company should be able to achieve meet its targets comfortably, considering that sales following the completion of SHED’s MCB and the growing rising sales of GBS-007. The necessary financing has already been completed for this purpose.
◇ Review of the medium-term strategic plan: KWB 2.0
The company revealed an update of its medium-term strategic plan, KWB 2.0, at the time of the result announcement for FY2022/3. The revision (KWB2.0) is aimed at the early realisation of the company’s vision “KIDS WELL, ALL WELL”.
Under KWB 2.0, the company will continue its existing biosimilars and new biologics business but will drive investment more in the SHED (cell therapy) business, aiming to become a unique company that creates cell therapy and gene therapy products based on SHED.
To this end, the company aims to: 1) establish a stable supply system for SHED, the raw material for first-generation SHED, as soon as possible by completing MCB, with the aim of early commercialisation of first-generation SHED; 2) create next-generation technologies to commercialise second-generation SHED; 3) strengthen its development system with a view to establishing personnel and overseas bases; 4) raise funds, including overseas equity finance, to implement the strategy.
New measures such as clinical development overseas through the establishment of overseas bases and the fostering of networks with overseas medical institutions and academia have been announced. These will require investment and development funds in Japan and a considerable amount of funds for the company’s overseas operations. Therefore, the company is considering financing methods not only domestically but also with an eye on overseas markets.
At the time of the 1Q result report, there was no announcement beyond the fact that MCB development was in its final stages. However, the company has stated that it will announce details of KWB 2.0 when it reveals 2Q results, which are expected in November 2022. We are interested to see the details of the new strategic plan.
◇Share price
As noted in the 4Q FY2022/3 research note, the company’s share price fell sharply due to as the postponement of the company’s initial indication to return to profitability in FY2023/3 dissapointed. Even after the 1Q results announcement, the share price has struggled to recover and the shares’ PBR has fallen well below its three-year average of 9.24. On the other hand, near-term sales of GBS-007 are robust and the company is making good progress against its full-year forecasts. If the company’s solid progress in its SHED business is confirmed by the completion of the MCB and other factors, there should be signs of a share price reversal in the future.
Relative share price (4584, TOPIX)
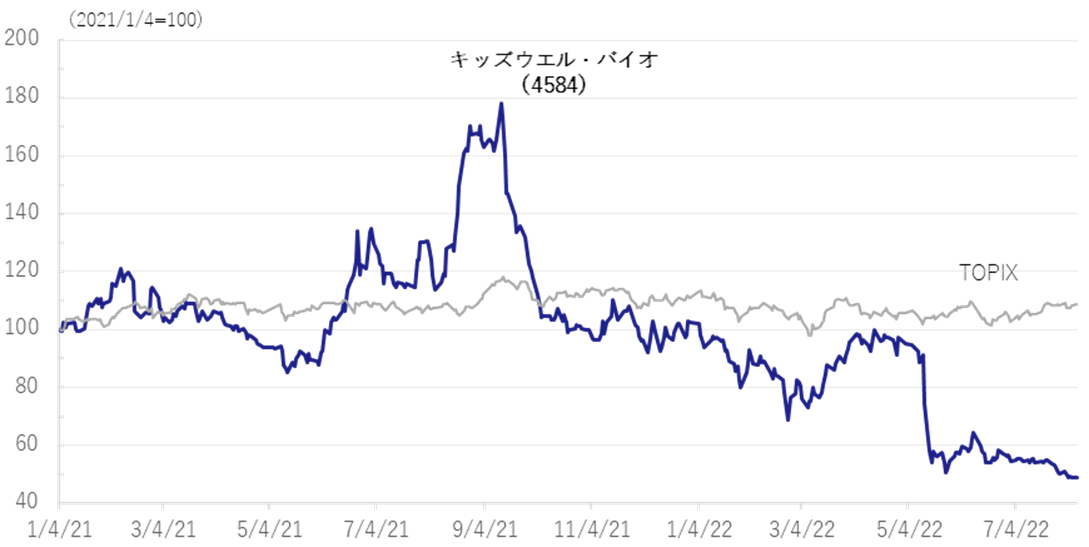
Historical PBR(4584, last three years, LTM)
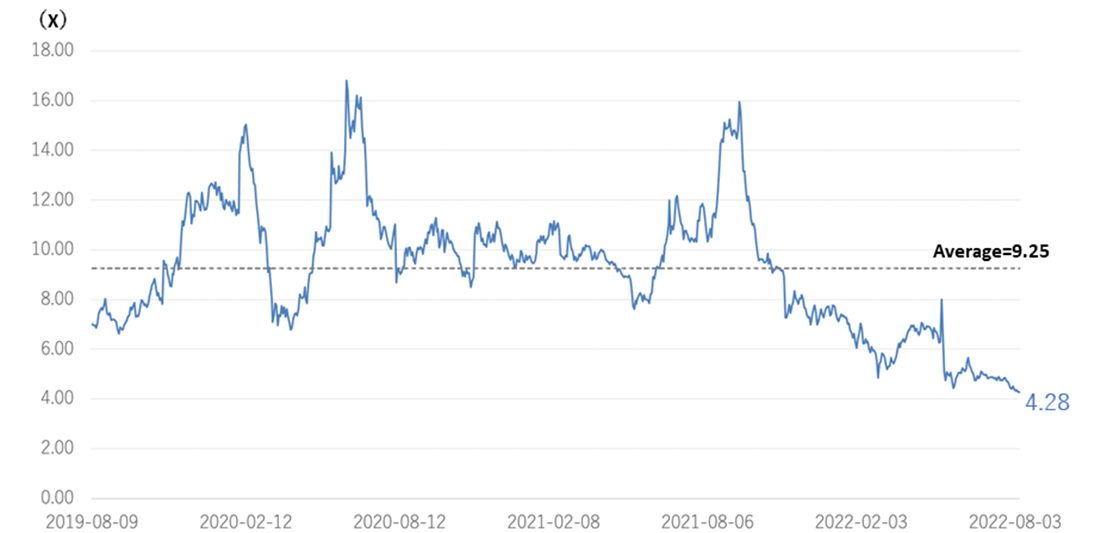
Pipeline
New biologics business
Biosimilar business
Regenerative Medicine business(Cell Therapy)
Financial data
| FY (¥mn) | 2020/3 | 2021/3 | 2022/3 | 2023/3 | |||||||||
| 1Q | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q | 1Q | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q | 1Q | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q | 1Q | |
| [Statements of income] | |||||||||||||
| Net sales | 284 | 30 | 419 | 345 | 121 | 53 | 547 | 276 | 303 | 438 | 642 | 186 | 610 |
| Cost of sales | 77 | 8 | 359 | 209 | 5 | 35 | 46 | 34 | 122 | 154 | 183 | 91 | 292 |
| Gross profit | 207 | 22 | 60 | 136 | 116 | 19 | 500 | 242 | 182 | 283 | 460 | 94 | 318 |
| SG&A expenses | 417 | 423 | 381 | 365 | 354 | 463 | 465 | 565 | 491 | 425 | 442 | 580 | 356 |
| R&D expenses | 235 | 249 | 201 | 213 | 138 | 265 | 198 | 363 | 297 | 236 | 237 | 380 | 105 |
| Operating profit (loss) | -210 | -401 | -321 | -229 | -238 | -445 | 36 | -323 | -309 | -142 | 18 | -486 | -37 |
| Non-operating income | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Non-operating expenses | 2 | 1 | 20 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 15 | 7 | 43 |
| Ordinary profit (loss) | -212 | -402 | -340 | -233 | -244 | -450 | 33 | -330 | -314 | -150 | 4 | -493 | -80 |
| Extraordinary income | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 418 | 0 | – | ||||||
| Extraordinary expenses | 5,939 | 0 | 0 | 194 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 0 | – | ||||
| Profit (loss) before income taxes | -6,147 | -402 | -340 | -425 | -244 | -451 | 26 | -331 | -314 | -148 | 421 | -493 | -80 |
| Total income taxes | 1 | 0 | 3 | -2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 52 | -51 | 0 |
| Net profit (loss) | -6,147 | -403 | -342 | -424 | -245 | -451 | 25 | -330 | -314 | -149 | 369 | -441 | -80 |
| [Balance Sheets] | |||||||||||||
| Current assets | 2,761 | 2,390 | 3,238 | 3,322 | 3,573 | 3,218 | 3,329 | 3,346 | 2,794 | 3,203 | 3,722 | 3,326 | 4,079 |
| Cash equivalents and short-term securities |
1,654 | 1,602 | 2,482 | 2,033 | 2,658 | 2,502 | 1,830 | 1,461 | 874 | 974 | 1,253 | 1,187 | 1,532 |
| Non-current assets | 330 | 427 | 418 | 270 | 379 | 393 | 340 | 588 | 728 | 656 | 178 | 177 | 225 |
| Tangible assets | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Investments and other assets | 328 | 425 | 416 | 268 | 374 | 389 | 336 | 582 | 722 | 651 | 173 | 173 | 220 |
| Total assets | 3,091 | 2,817 | 3,656 | 3,592 | 3,952 | 3,611 | 3,670 | 3,934 | 3,522 | 3,859 | 3,901 | 3,503 | 4,304 |
| Current liabilities | 421 | 550 | 529 | 881 | 772 | 858 | 925 | 1,114 | 823 | 1,034 | 1,045 | 1,129 | 1,175 |
| Short-term borrowings | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | ||||||||
| Long-term debts to be repaid within one year |
75 | 250 | |||||||||||
| Non-current liabilities | 25 | 24 | 1,224 | 1,224 | 1,384 | 1,287 | 1,231 | 1,209 | 1,051 | 826 | 718 | 656 | 1,485 |
| Long-term debt | 1,200 | 1,200 | 1,340 | 1,240 | 1,200 | 1,100 | 900 | 700 | 700 | 625 | 1,450 | ||
| Long-term borrowing | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 525 | 1,350 | ||
| Convertible bonds | 600 | 600 | 740 | 640 | 600 | 500 | 300 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Total liabilities | 446 | 573 | 1,752 | 2,105 | 2,156 | 2,145 | 2,156 | 2,324 | 1,873 | 1,860 | 1,763 | 1,785 | 2,661 |
| Total net assets | 2,644 | 2,244 | 1,904 | 1,487 | 1,796 | 1,466 | 1,514 | 1,610 | 1,648 | 1,999 | 2,138 | 1,719 | 1,643 |
| Total shareholders’ equity | 2,644 | 2,244 | 1,904 | 1,487 | 1,796 | 1,466 | 1,514 | 1,610 | 1,648 | 1,999 | 2,138 | 1,719 | 1,444 |
| Capital | 612 | 612 | 612 | 612 | 842 | 892 | 912 | 1,032 | 1,150 | 1,420 | 1,420 | 1,421 | 1,424 |
| Legal capital reserve | 9,917 | 9,917 | 9,917 | 9,917 | 10,147 | 10,197 | 10,217 | 10,338 | 10,456 | 10,725 | 10,726 | 10,727 | 10.730 |
| Retained earnings | -7,908 | -8,311 | -8,653 | -9,077 | -9,322 | -9,773 | -9,748 | -10,079 | -10,393 | -10,542 | -10,173 | -10,614 | -10.710 |
| Stock acquisition right | 38 | 43 | 51 | 57 | 70 | 82 | 101 | 116 | 134 | 145 | 165 | 185 | 199 |
| Total liabilities and net assets | 3,091 | 2,817 | 3,656 | 3,592 | 3,952 | 3,611 | 3,670 | 3,934 | 3,522 | 3,859 | 3,901 | 3,503 | 4,304 |
| [Statements of cash flows] | |||||||||||||
| Cash flow from operating activities | -604 | -1,325 | -104 | -1,267 | -857 | -1,169 | |||||||
| Loss before income taxes | -6,548 | -7,314 | -695 | -999 | -462 | -533 | |||||||
| Cash flow from investing activities | -106 | -137 | -5 | -22 | – | 526 | |||||||
| Expenditure on acquisition of intangiblefixed assets |
– | – | -3 | -3 | – | -1 | |||||||
| Purchase of investment securities | -100 | -100 | – | – | – | – | |||||||
| Sales of investment securities | – | – | – | – | – | 526 | |||||||
| Cash flow from financing activities | 40 | 1,221 | 579 | 718 | 370 | 369 | |||||||
| Income from the issuance of convertible bond-type bonds with stock acquisition rights |
– | 599 | 599 | 599 | – | – | |||||||
| Income from issuance of shares by exercising stock acquisition rights |
40 | 40 | – | 138 | 370 | 369 | |||||||
| Income from issuance of stock acquisition rights |
– | 3 | 4 | 4 | – | – | |||||||
| Net increase in cash and cash equiv. | -670 | -240 | 468 | -571 | -486 | -273 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equiv. at beginning of period | 2,009 | 2,009 | 2,032 | 2,032 | 1,461 | 1,462 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equiv. at end of period | 1,602 | 2,032 | 2,501 | 1,461 | 974 | 1,187 |
Note: Consolidated basis until FY2022/3; non-consolidated basis from 1Q FY2023/3. For the statement of cash flows, the figures for 2Q are the cumulative figures for the period from 1Q to 2Q, and the figures for 4Q are the cumulative figures for the period from 1Q to 4Q. Therefore, the opening balance is also the balance at the beginning of each quarter.
Source: Omega Investment from company materials.
