Cosmo Bio (Company note – basic)

| Share price (17/4) | ¥948 | Dividend Yield (12/23 CE) | 3.16 % |
| 52weeks high/low | ¥1,117/940 | ROE(12/22) | 6.52 % |
| Avg Vol (3 month) | 6.81 thou shrs | Operating margin (12/22) | 8.55 % |
| Market Cap | ¥5.7 bn | Beta (5Y Monthly) | 0.63 |
| Enterprise Value | ¥3.1 bn | Shares Outstanding | 6.048 mn shrs |
| PER (12/23 CE) | 12.25 X | Listed market | TSE Standard |
| PBR (12/22 act) | 0.68 X |
| Click here for the PDF version of this page |
| PDF Version |
Contribute to the advancement of life sciences by providing research reagents and life science equipment
Summary
◇Cosmo Bio Co., Ltd is a trading company specialising in the life sciences with the aim of “Contribute to the advancement of life sciences”. Founded in 1983 as a subsidiary of the former Maruzen Oil, the company went through an MBO and is now an independent, specialised trading company. Its main products are research reagents used by pharmaceutical companies, universities, research institutions and other research facilities, which account for approximately 80% of sales. The company procures over 12 million products and services from 600 suppliers, including overseas suppliers, and provides them to life science researchers. The company’s strengths lie in its overseas supplier network, which it has built up over many years of sales activities, and the trustworthy relationships that enable it to identify its domestic customers’ needs accurately. In recent years, the company has moved beyond the mere function of a trading company to create greater added value by manufacturing products and services required by its customers in-house or providing contract services.
◇Reagent market expected to grow steadily: The domestic life science research reagent market is estimated to be worth approximately 120 billion yen and is growing at an annual rate of around 3%. Rapid growth is not expected, but stable growth is expected over the long term. Long-term steady growth is expected given trends in R&D expenditure by pharmaceutical companies (CAGR = 4% over the past ten years), which are the users, and in scientific research expenditure, which is an indicator of the budgets of universities and research institutions.
Players in this market include Japanese subsidiaries of foreign reagent manufacturers, subsidiaries or business units of major Japanese chemical manufacturers, and independent trading companies, including the company. Currently, the company’s market share is estimated at around 5%.
◇Risk factors: Although the life science research reagent market is expected to grow steadily, several risks must be considered. Many reagents are supplied to biotechnology-related venture companies in North America. However, restructuring through mergers and acquisitions is routine in this field, and commercial rights may be lost due to changes in their shareholders. In addition, the head office may establish a corporation directly in Japan. Second is the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. Although the company has taken measures such as forward exchange contracts under specific internal rules, the rapid depreciation of the yen since spring 2022 has led to an increase in payments against the dollar and a significant rise in costs, which weighed on profits. Measures are being taken to neutralise foreign exchange risks, such as expanding exports abroad.
◇In FY12/2022, sales were 9.55 billion yen, up 3.5% YoY, while operating profit was 0.8 billion yen, down 22%. Sales increased due to the growth of research reagents. However, the rises in COGS and other costs due to the weak yen weighed on profits. The company cautiously forecasts the exchange rates in FY12/2023 and expects a 2.6% increase in sales and a 26.5% decline in operating profit.
◇New Three-Year Plan: The company has formulated and announced a new Three-Year Plan, with FY12/2023 as the first year. The plan aims to “Contribute to the advancement of life sciences”. It sets out a concrete long-term strategy to create products and services that will become new pillars of growth, enter non-research-use markets focusing on life sciences, and expand overseas operations, including export business. The company aims to grow further by developing its manufacturing, sales, contract services, and exports.
◇Share price observation: The company’s shares have traded in a box range of around 1,000 yen for the past year. The low trading volume is also a concern. The life science research reagent market is expected to grow steadily, and the company’s financial strength is solid and reassuring. However, inactive trading is thought to be due to difficulty finding growth drivers. Going forward, the share price may well be revalued as the company implements its new Three-Year Plan and progresses with new measures to increase earnings, including exports.
Table of contents
| Summary | 1 |
| Key financial data | 2 |
| Company profile | 3 |
| History/Breakdown of most recent sales/Company’s group | 3 |
| Business overview | 5 |
| Japanese research reagent market/products and services | 5 |
| Corporate uniqueness/strengths/risk factors | 7 |
| Earnings trend | 9 |
| Financial results | 10 |
| Full-year results for FY2022/12 | 10 |
| FY2023/12 full-year forecast | 10 |
| Growth strategy | 11 |
| Share price trend | 13 |
| Financial data | 15 |
| Corporate data | 16 |
| Corporate profile/history | 16 |
| The top management and Corporate governance | 17 |
| Major shareholders, Shareholding by ownership, Shareholder return policy | 18 |
Key financial data
| Fiscal Year | 2017/12 | 2018/12 | 2019/12 | 2020/12 | 2021/12 | 2022/12 |
| Net sales | 7,068 | 7,261 | 7,590 | 8,092 | 9,231 | 9,553 |
| Cost of sales | 4,535 | 4,602 | 4,710 | 4,940 | 5,572 | 6,112 |
| Gross profit | 2,532 | 2,659 | 2,879 | 3,152 | 3,658 | 3,440 |
| SG&A expenses | 2,339 | 2,330 | 2,474 | 2,399 | 2,609 | 2,624 |
| Operating income | 193 | 328 | 405 | 752 | 1,048 | 816 |
| Ordinary income | 397 | 403 | 470 | 817 | 1,099 | 790 |
| Net profit before taxes | 400 | 403 | 388 | 1,008 | 1,099 | 790 |
| Net profit attributable to owners of the parent |
237 | 260 | 237 | 674 | 737 | 517 |
| Current assets | 5,143 | 5,668 | 5,927 | 6,756 | 7,310 | 7,136 |
| Cash and deposits | 1,483 | 2,268 | 2,516 | 3,259 | 3,555 | 3,036 |
| Non-current assets | 2,982 | 2,832 | 2,962 | 2,883 | 2,761 | 3,176 |
| Total assets | 8,126 | 8,501 | 8,890 | 9,640 | 10,072 | 10,313 |
| Total liabilities | 1,288 | 1,448 | 1,568 | 1,779 | 1,752 | 1,695 |
| Total net assets | 6,838 | 7,053 | 7,321 | 7,861 | 8,319 | 8,617 |
| Equity ratio (%) | 78.5% | 77.4% | 77.0% | 76.3% | 77.3% | 78.1% |
| Cash flow from operating activities | 89 | 908 | 549 | 803 | 648 | 284 |
| Cash flow from investing activities | -235 | -185 | -115 | 42 | -145 | -291 |
| Cash flow from financing activities | -109 | -85 | -85 | -97 | -420 | -236 |
| Increase/decrease in cash and cash equivalents |
-264 | 684 | 348 | 743 | 95 | -218 |
Source: Omega Investment from company materials
Company profile
Cosmo Bio is a trading company specialising in the life-science field, focusing on reagents*, with the Group’s objective of ‘Contribute to the advancement of life sciences’. Its main business is purchasing and wholesale research reagents, equipment, contract services and clinical reagents related to life sciences. Reagents’ market size is different from those of diagnostics and therapeutics. Still, they are essential products and services indispensable for life science researchers worldwide to develop new drugs.
History
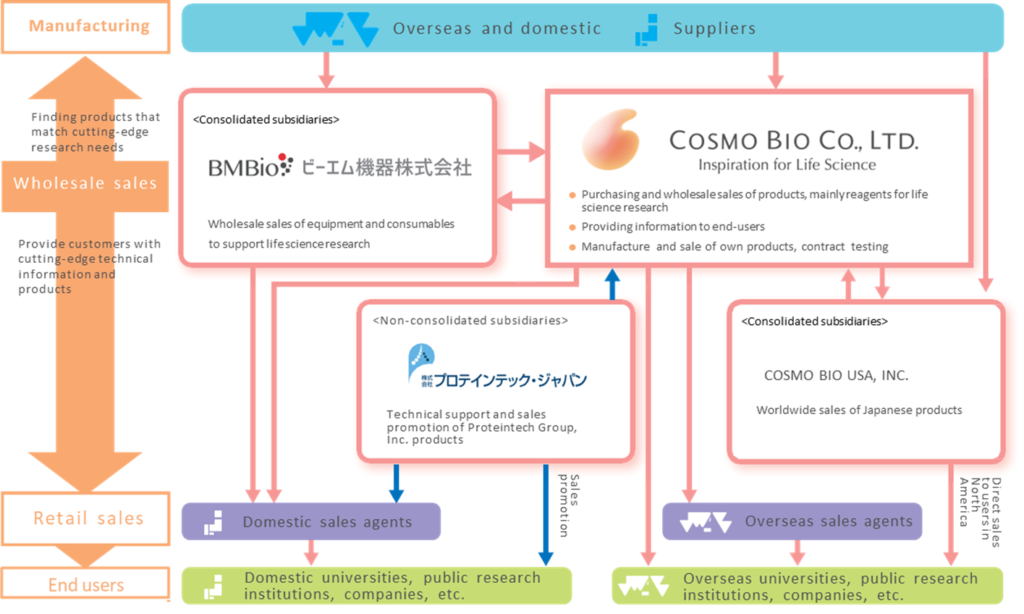
The company’s history can be traced back to 1983 when it was founded as Maruzen Oil Biochemical Co., Ltd as a subsidiary of the former Maruzen Oil (now Cosmo Oil) for basic biotechnology research reagent business. The company subsequently renamed itself to Cosmo Bio Co., Ltd. (1985) following a merger and restructuring of the parent company. In September 2000, the company became independent from Cosmo Oil through an MBO. In August 2004, it established Cosmo Bio USA, Inc. in San Diego, California, one of the world’s leading bioresearch centres and the location of many bio-ventures. It was made a base to search for reagents and promote the export of Japanese-made reagents. In September 2005, the company was listed on the JASDAQ market. Subsequently, the company expanded its operations by investing in and merging with companies in related fields. In December 2006, Primary Cell Co., Ltd. became a subsidiary, and Cosmo Bio entered the manufacturing business. In March 2010, BM Equipment Co., Ltd. was consolidated as a trading subsidiary that imports equipment and consumables for life science research. In October 2017, the company relocated and consolidated its Sapporo business facilities and opened the Sapporo Office, establishing a structure to reinforce its recent focus on contract services and manufacturing and sales. (See also the Alignment Chart on p. 16)
Breakdown of most recent sales
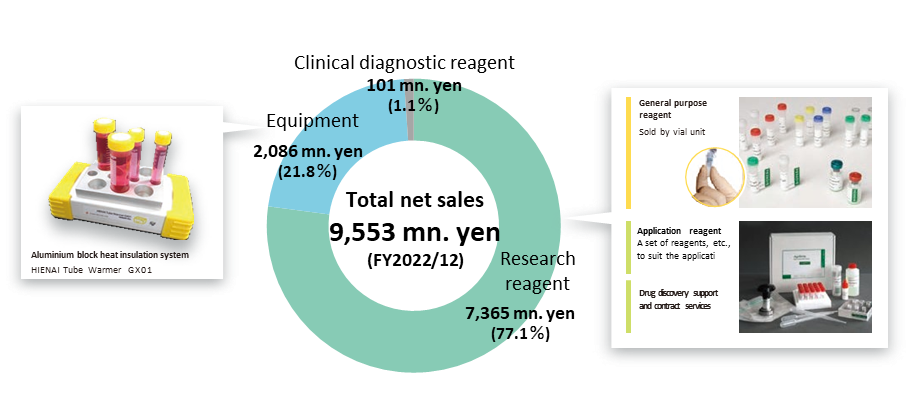
FY12/2022 sales were 9,553 million yen. Although the company operates in a single segment, it discloses a breakdown of sales by product – research reagents, equipment and clinical diagnostics. Research reagents account for 77%, equipment for 22% and clinical diagnostics 1%.
Breakdown of sales by product
*Reagents: according to the Japan Reagents Association, reagents are legally defined as ‘chemical substances used for the detection or quantification of substances by chemical methods, experiments in the synthesis of substances or for physical properties’.
The general concept is also defined as “chemicals used for measurement standards, detection and confirmation of substances, quantification, separation and purification, synthesis experiments and measurement of physical properties in testing and research cases, such as inspection, testing, research and experiments, in the form of supply suitable for small quantities with guaranteed quality for the respective purpose of use”. More specifically, they are agents used for experiments, research, and measurements and include chemical substances, components extracted from the body of a living organism (proteins, cells, nucleic acids, etc.), and solvents used to react with them. Reagents for life science are mainly extracted from living organisms or synthesised from such substances and are supplied in small quantities, such as several tens of micrograms.
On the other hand, diagnostic reagents are drugs doctors use in various tests to diagnose health or disease conditions. They are also known as in vitro diagnostic drugs or clinical diagnostic reagents and are distinguished from reagents.Generally, we take therapeutic drugs (ethical drugs) to cure diseases. They are administered to treat various diseases and are researched, developed, manufactured, and marketed by major national and international pharmaceutical companies.
The domestic market for life science research reagents is around 120 billion yen (2021, company data), the market size for diagnostics is about 800 billion yen (2021, Japan Association of Clinical Reagents Industries
Company’s group
The company’s group comprises Cosmo Bio (the company), two consolidated subsidiaries: BM Equipment and Cosmo Bio USA, Inc., and the non-consolidated subsidiary Proteintech Japan Co., Ltd. For their respective businesses and product flows, see the diagram below. BM Equipment and Proteintech Japan are located on the same floor in the head office in Koto-ku, Tokyo, where Cosmo Bio is based, to facilitate communication as a group.
Life science research and User demographic
In addition to Koto-ku, Tokyo, mentioned above, where the company’s head office is located, the company’s other operating bases include the Sapporo Office and the Shinsuna Logistics Centre. As mentioned in history, the Sapporo Office (Otaru, Hokkaido) was established in October 2017 by relocating and consolidating the company’s Sapporo area business facilities. The facility is responsible for contract services and manufacturing and sales, which are the company’s growth areas of focus.
The Shinsuna Distribution Centre was opened in January 2013. The company runs a system to hold an inventory of hot-selling products (the Group’s products and inventory on its BS at end-December 2022 amounted to about 1 billion yen) and ship them. The company can respond precisely to the needs of pharmaceutical companies, universities, and research institutions, which often require prompt deliveries.

Business overview
Provides essential reagents and equipment for life science researchers worldwide
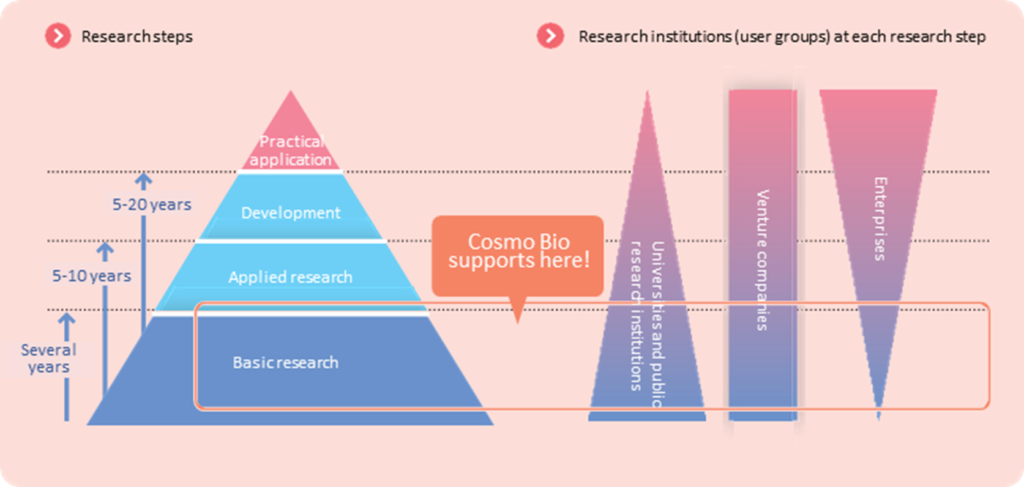
The company provides life science researchers worldwide with research reagents integral to the basic research process. As is well known, developing pharmaceuticals to save lives and improve QoL usually takes a long time – more than ten years – through basic research, applied research, development and clinical trials. In recent years, the development of antibody medicines and the linkage with IT, such as in silico (including the application of quantum computers to accelerate the process), is expected to be utilised. However, ongoing research activities in the research field are vitally necessary.
The reagents and equipment provided by the company are essential items for basic research at pharmaceutical companies, universities, and research institutions. Although the demand will not grow rapidly, it should allow the company to secure a stable profit margin.
Overview of the company’s group and product flow
Japanese life science research reagents market
See the figure below for the domestic life science research reagents market size and players. In the past, the market has grown at a CAGR of around 3% and is estimated to be worth about 120 billion yen in 2021. Players and their market shares in this field are shown in the diagram below right. Japanese subsidiaries of reagent companies in North America and elsewhere account for a large percentage of the market. At the same time, group companies or business divisions of major Japanese chemical manufacturers acquired through acquisitions in recent years also command some shares. Two independent specialist trading companies are in the Top 10, including the company with a market share estimated at around 5%. Competition is intense, but they all have their areas of expertise and can enjoy certain levels of sales and profits.
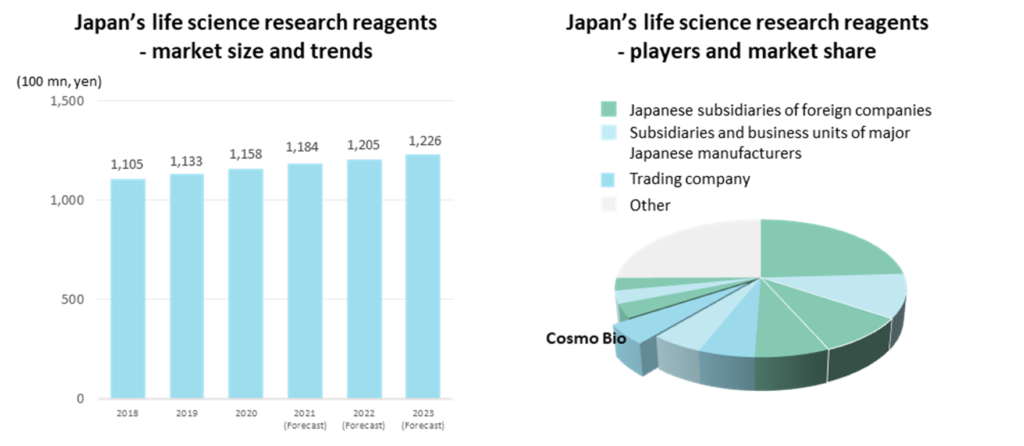
Next examines the status of the reagents’ users. As mentioned, the customers of reagents are pharmaceutical companies, universities, research institutions and other research facilities in the life sciences sector. First, a look at the R&D investment trends of Japan’s major pharmaceutical companies is as follows. The total R&D expenditure of the top 10 companies is estimated to be over 2 trillion yen in 2021. R&D investment by the major pharmaceutical companies is enormous, with the leading figures in 2021 being 526.1 billion yen by Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (up 15.4% YoY), 260.2 billion yen by Daiichi Sankyo Company Ltd. (up 14.4%) and 246 billion yen by Astellas Pharma Inc. (up 9.6%). As the ten largest companies account for approximately 90% of the R&D expenditure of Japanese pharmaceutical companies, one can assume that the trends of the major players are broadly in line with those of the market. The growth has been stable and steady, averaging +4.0% over the last ten years.
Trends in research and development expenditure of major domestic pharmaceutical companies
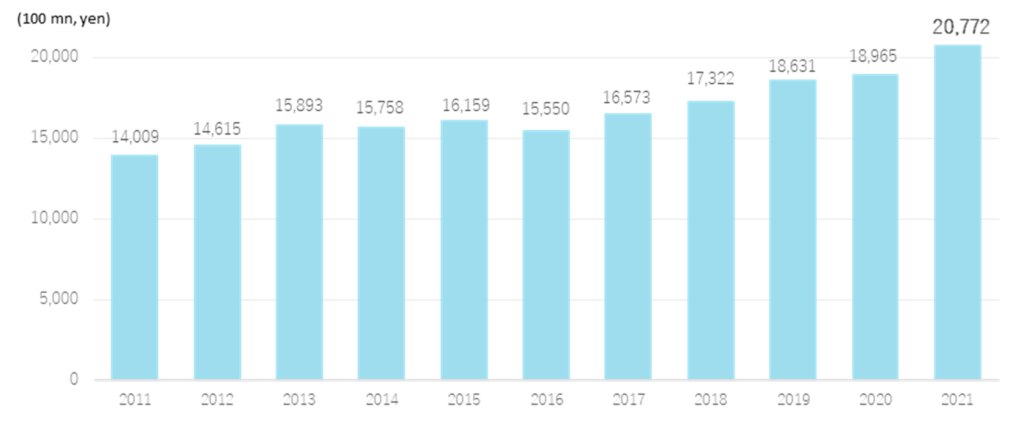
Source: Prepared by Omega Investment from the companies’ annual reports.
Trends in Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) at Japanese universities and educational institutions are as follows. University-related budgets have often been cut, but Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research is on an increasing trend to meet the modern demands of academia and to promote innovation while implementing institutional reforms.
With the trends in R&D expenditures of large pharmaceutical companies put together, the reagent market for life science research can be regarded as a stable growth market.
Trends in Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research

The range of products and services offered by the company
The company introduces 12 million state-of-the-art products from some 600 suppliers worldwide, adds its value and provides them to life science researchers through its approximately 200 distributors. Examples of current products and services are as follows.

Corporate uniqueness/strengths
Strong relationships of trust with clients and suppliers: In research and development, where reagents are used, a single reagent is rarely used in large quantities. A variety of reagents in microgram quantities are required at each research level. To meet the needs of such users, a large assortment of reagents is required, but this cannot be achieved overnight – it is only possible after 40 years of building trusting relationships with clients and solid relationships with suppliers of cutting-edge reagents, mainly in North America.
Providing state-of-the-art information in the life-science field: Related to the above, as reagents are used in cutting-edge research, it is still critical to have state-of-the-art information and knowledge on life sciences. As a trading company specialising in life sciences, in addition to the information gathering capabilities of its head office, the company, in cooperation with Cosmo Bio USA, Inc., exhibits at and participates in various bio-related events and provides cutting-edge information in the life sciences field to capture the needs of its clients ahead of competitors.
Responding to user needs by manufacturing and developing in-house products: Although import trading is the company’s primary function, the company also produces and sells cells that cannot be replaced by imported cells and provides contract services using cells. The company plans to focus more on manufacturing and selling such in-house products and contract services, aiming for further growth.
Accumulation and possession of various know-how related to the reagent business: Products in the life sciences sector, especially those related to reagents, require different knowledge and know-how than the import and export of ordinary products. Many of the products handled by the company need to comply with various laws and administrative guidance, such as the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act (Act on Securing Quality, Efficacy and Safety of Products Including Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices), the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act and the Narcotics and Psychotropics Control Act. These laws vary from country to country, and knowledge and information on the differences between countries are also important. In addition, some reagents are of animal origin and are subject to animal quarantine. Furthermore, some reagents, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and cells, are of biological origins. Appropriate temperature control is required, such as packing dry ice during international transport procedures. The company’s know-how and expertise in these reagents are one of its strengths.
Risk factor
On the other hand, the following factors are considered risk factors and require attention.
Risks from mergers and acquisitions of suppliers: 400 of the company’s 600 suppliers are overseas and are mainly North American. Companies that manufacture and supply reagents are bio-ventures; shareholders may sell the business at any given time, depending on the circumstances. As a result, the company may lose its commercial rights because of a change in enterprise ownership. Also, a foreign supplier could establish its domestic sales network or switch to a competing trading company. The company has established and maintains various relationships of trust to secure a stable supply of products, but investors should be aware of these risks.
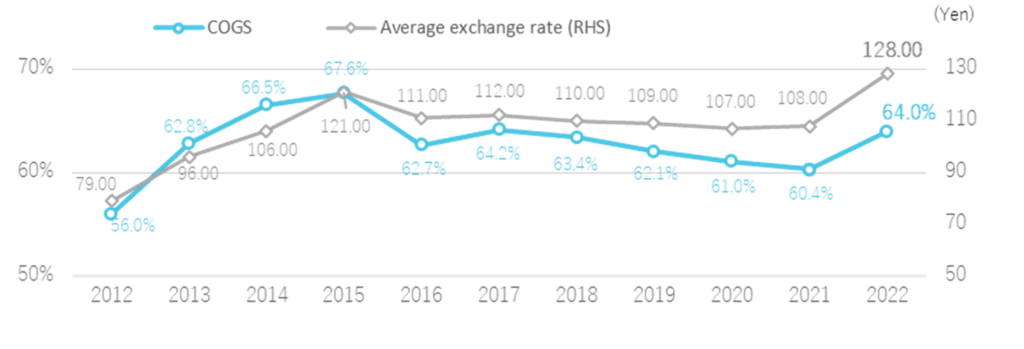
Foreign exchange risk: Most of the company group’s products are imported goods settled in foreign currencies, so the cost of sales is surrendered to exchange rate fluctuations. The company hedges by forward exchange contracts within a certain proportion of actual demand by its internal policy. However, a sharp depreciation of the yen, such as the one from mid-2022, would sharply raise the cost of sales and significantly impact business performance. (See chart below)
Competition risk: Competition is intense in the domestic life science research products market. As noted about the risk of suppliers, collecting state-of-the-art information in the life sciences sector and searching for and finding research reagents that clients will need in the future is essential to survive in this industry. To this end, it is necessary to differentiate the company by strengthening its marketing capabilities and introducing new products on time.
Regulatory risk: As noted in the section on corporate uniqueness and strengths, some of the products handled by the company are required to comply with various laws and regulations. The company is aware of the importance of these regulations and always takes careful measures to comply with them. Still, there is a possibility that an accident or other event could lead to a breach of these laws and regulations. If these laws and regulations are amended, new measures will be required.
The Yen-dollar exchange rate and COGS ratio
Sales/Profit by Segment
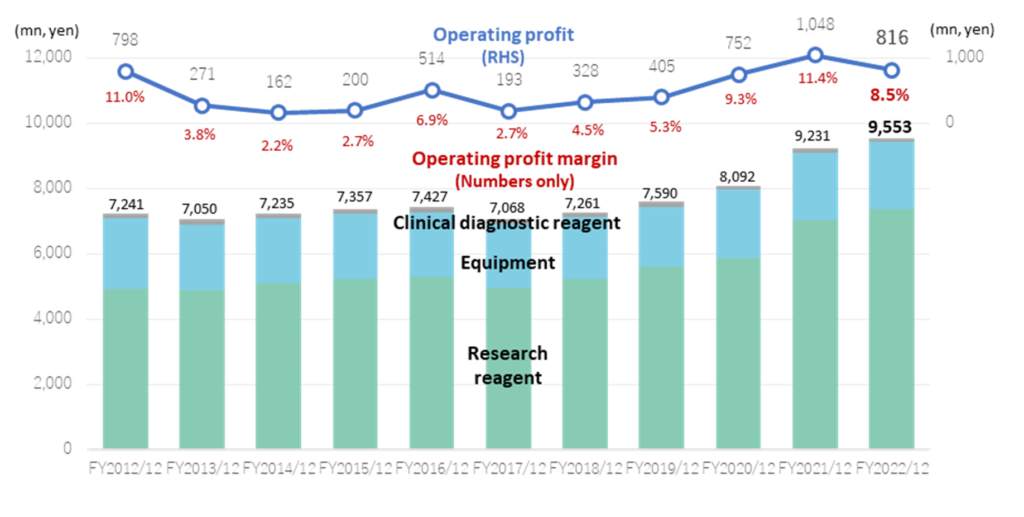
Earnings trend
The company’s financial trends are shown in the diagram above. Sales had been in the region of 7 billion yen until FY 12/2019 but reached 8 billion yen in FY 12/2020 and over 9 billion yen in FY12/2021 and FY12/2022. Since the spring of 2020, COVID-19 has significantly impacted companies in other industries, and many have experienced a significant decline in sales. However, the impact appears to have been limited for the company. The reasons were: 1) products used in research facilities, such as reagents, have a long-term demand and are not easily affected by restrictions on sales activities due to infectious diseases; 2) demand for research consumables and other products increased in relation to the spread of pandemic disease, and these products registered robust sales; 3) contract services to conduct tests on behalf of researchers and deliver the results were strong. In addition, at the beginning of 2020, shipments from suppliers, particularly in China, stagnated. There was a temporary global shortage of research consumables and other products, but this has since recovered.
Sales grew at a CAGR of 2.8% over the ten years to FY12/2022. Research reagents grew at a steady CAGR of 4.1%. Regarding the operating profit, the company posted an OP margin of over 5% from FY 12/2019 onwards, partly thanks to the yen strength that continued until FY12/2021. In FY12/2022, the OP margin declined due to the sharp yen depreciation from mid-2022, as shown in the diagram on the previous page.
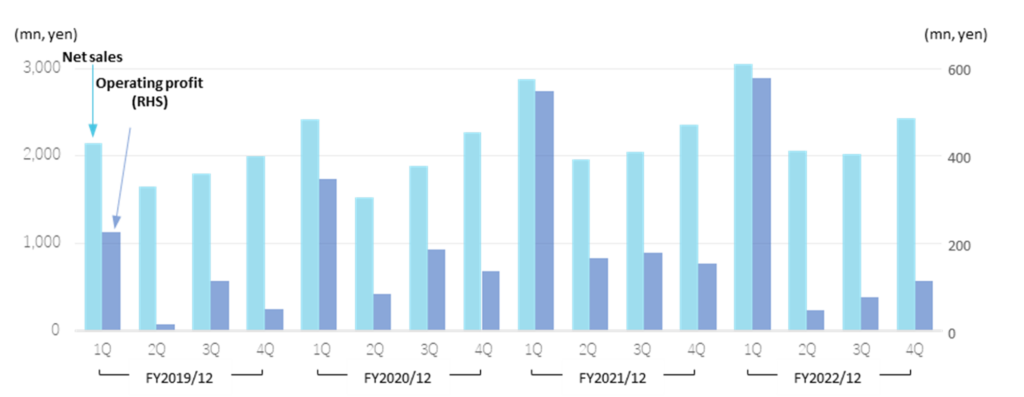
By quarter, sales and profits tend to rise sharply in 1Q. The company’s accounting year ends at the end of December. Still, as is well known, many universities, other public research institutions, and private companies close their books at the end of March. Hence, the company’s sales composition is characteristically high during January-March. Sales in 1Q tend to account for about 30% of the full-year total, while 1Q’s operating profit comprises about 50%. In FY12/2022, 1Q operating profit comprised 71% of the full-year record, partly due to the weaker yen in the second half of the fiscal year.
Sales/Profit by Segment (Quarterly basis)
Financial results
1) FY12/2022 financial results – 3.5% increase in sales and 22.2% decrease in operating profit
FY2022 results were a 3.5% YoY increase in sales to 9,553 million yen, a 22.2% decrease in operating profit to 816 million yen and a 29.8% decrease in profit attributable to owners of parent to 517 million yen. The main reason for the decline in profit was the yen depreciation.
Sales by product category were Research Reagents, 7,365 million yen, up 4.7% YoY, Equipment, 2,086 million yen, up 0.5% and Clinical diagnostics, 101 million yen, down 15.9%. In addition to domestic reagent sales, overseas sales were strong.
As per the PL, the COGS ratio increased by 3.6 percentage points, from 60.4% to 64.0%, due to the weaker yen. The yen significantly weakened YoY, from 108 yen in the previous year to 128 yen against the USD. Despite the negative impact of the weaker yen, overseas sales were strong, and the profit decline appears to have been milder than the company expected.
YoY factor analysis of operating profit changes shows that, over the FY2021 result of 1,048 million yen, the effect of higher sales was a positive 215 million yen, but the impact of the foreign exchange rate was a negative 404 million yen, and increased labour costs were a negative 24 million yen, with other costs a negative 19 million yen, resulting in the FY2022 OP of 816 million yen.
In BS, total assets at the end of December 2022 amounted to 10,313 million yen, an increase of 240 million yen YoY. This was because current assets decreased by 174 million yen (securities decreased by 300 million yen and merchandise and finished products increased by 249 million yen), while fixed assets increased by 415 million yen (investment securities increased by 436 million yen).The equity ratio at the end of FY2022 was 78.1%, little changed from 77.3% at the end of FY2021.
2) Forecast for FY12/2023 – The company expects a 2.6% increase in sales and a 26.5% decline in operating profit
The company’s forecasts for FY2023 are sales of 9.8 billion yen, up 2.6% YoY, operating profit of 600 million yen, down 26.5% and profit attributable to owners of parent of 450 million yen, down 13.0%.
As in FY2022, the main factor contributing to the decline in profits is the exchange rate, which the company has set at 140 yen to the dollar for FY2023. In anticipation of the severe depreciation of the yen, the company plans to overcome the negative impact of the exchange rate move by actively developing non-import self-made products and contract services, as well as expanding exports. While foreign currency moves cannot be precisely predicted, the company’s internal exchange rate of 140 yen to the dollar is a cautious assumption. Depending on actual exchange rates, there may be an upside in profits.
Profit and loss statement (incl. sales by product)
| Financial year | 2017/12 | 2018/12 | 2019/12 | 2020/12 | 2021/12 | 2022/12 | 2023/12 (Forecast) |
CAGR 2022/2017 |
| Net sales | 7,068 | 7,261 | 7,590 | 8,092 | 9,231 | 9,553 | 9,800 | 6.2% |
| YoY | -4.8% | 2.7% | 4.5% | 6.6% | 14.1% | 3.5% | 2.6% | |
| Research reagent | 4,947 | 5,216 | 5,613 | 5,872 | 7,035 | 7,365 | 8.3% | |
| Equipment | 1,981 | 1,903 | 1,836 | 2,099 | 2,075 | 2,086 | 1.0% | |
| Clinical diagnostic reagent | 139 | 141 | 140 | 119 | 120 | 101 | -6.2% | |
| Cost of sales | 4,535 | 4,602 | 4,710 | 4,940 | 5,572 | 6,112 | 6.2% | |
| Cost of sales ratio | 64.2% | 63.4% | 62.1% | 61.0% | 60.4% | 64.0% | ||
| Gross profit | 2,532 | 2,659 | 2,879 | 3,152 | 3,658 | 3,440 | 6.3% | |
| SG&A expenses | 2,339 | 2,330 | 2,474 | 2,399 | 2,609 | 2,624 | 2.3% | |
| Operating profit | 193 | 328 | 405 | 752 | 1,048 | 816 | 600 | 33.4% |
| YoY | -62.5% | 69.9% | 23.5% | 85.7% | 39.4% | -22.1% | -26.5% | |
| Operating profit margin | 2.7% | 4.5% | 5.3% | 9.3% | 11.4% | 8.5% | 6.1% | |
| Ordinary profit | 397 | 403 | 470 | 817 | 1,099 | 790 | 660 | 14.8% |
| Net profit before taxes | 400 | 403 | 388 | 1,008 | 1,099 | 790 | 14.6% | |
| Net profit attributable to owners of the parent |
237 | 260 | 237 | 674 | 737 | 517 | 450 | 16.9% |
| YoY | -6.7% | 9.7% | -8.8% | 184.4% | 9.3% | -29.9% | -13.0% | |
| Profit margin | 3.4% | 3.6% | 3.1% | 8.3% | 8.0% | 5.4% | 4.6% |
(Unit: mn, yen)
Source: Omega Investment from company materials
Financial trend
| JPY, mn, % | Net sales | YoY % |
Oper. profit |
YoY % |
Ord. profit |
YoY % |
Profit ATOP |
YoY % |
EPS (¥) |
DPS (¥) |
| 2018/12 | 7,261 | 2.7 | 328 | 70.1 | 403 | 1.6 | 260 | 9.4 | 43.93 | 14.00 |
| 2019/12 | 7,590 | 4.5 | 405 | 23.5 | 470 | 16.5 | 237 | -8.6 | 40.14 | 14.00 |
| 2020/12 | 8,092 | 6.6 | 752 | 85.6 | 817 | 73.7 | 674 | 183.2 | 113.70 | 34.00 |
| 2021/12 | 9,231 | 14.1 | 1,048 | 39.4 | 1,099 | 34.5 | 737 | 9.4 | 126.94 | 36.00 |
| 2022/12 | 9,553 | 3.5 | 816 | -22.2 | 790 | -28.1 | 517 | -29.8 | 89.13 | 36.00 |
| 2023/12 (CE) | 9,800 | 2.6 | 600 | -26.5 | 660 | -16.5 | 450 | 13.0 | 77.41 | 30.00 |
Growth strategy
1) New Three-Year Plan (2023-2025): ‘Contribute to the advancement of life sciences‘ as the Group’s objective
The company announced its new Three-Year Plan (2023-2025) at the time of the FY2022 result announcement. First, the previous Three-Year Plan, which ended in FY2022, was reviewed. That called for 1) the creation of new business foundations, 2) the strengthening of trading and manufacturing functions, and 3) the enhancement of corporate value. However, as the three-year period coincided with the pandemic disease, the company could not carry out many of the tasks planned. On the other hand, the introduction of remote working and other aspects of operational efficiency has enabled the company to make rapid progress, which will contribute to strengthening the company’s revenue base. It is worth noting that even in such an environment, sales increased by 25.8% compared to FY2019, and operating profit increased by 48.1% despite the rapid depreciation of the yen during FY2022, which weighed on profits.
Achievements include 1) as a creation of a new business platform, VHH antibody screening technology was transferred from MeSCue-Janusys Inc. to launch the service by the end of 2023. Also, 2-1) to strengthen trading, the integration of the customer information management system (CRM) was achieved, and practical sales activities, etc., using CRM information have progressed. And 2-2) to strengthen manufacturing, an important agenda for the company’s growth strategy, the company acquired the software assets of an epitope analysis system and is currently developing improvements. In addition, the company published a paper on the results of joint research on infection-control substances for COVID-19, which it has conducted in collaboration with Osaka Metropolitan University. Other progress has also been made to strengthen the catalogue product line-up.
As to 3) to enhance corporate value, progress has been made in reforming working methods, personnel systems, and human resources development. In addition, as part of efforts to strengthen governance, the company has turned a company with an audit committee. Furthermore, share buybacks were implemented in consideration of shareholder returns.
Thus, the previous Three-Year Plan achieved results, albeit during the pandemic disease.
The new Three-Year Plan, starting in FY2023, sets out the Group’s objective to “Contribute to the advancement of life sciences” and further defines the Group’s philosophy and policies. The concrete long-term strategy is to 1) create products and services that will become new pillars of growth, 2) expand into non-research markets with a focus on life sciences, 3) strengthen synergies between group companies, 4) expand overseas operations, including export business, and 5) realise stable and sustainable growth.
See the diagram on the next page for the company’s business matrix. The trading company function, centred on the products in the bottom left-hand corner, has been the company’s main business to date and is already a big tree. The trading company function is a stable business. Still, it is a so-called margin business, with limited profit margins, albeit higher than commodities reflecting the high-tech nature of life sciences. It is also susceptible to currency fluctuations, as in FY2022.
Meanwhile, businesses related to the manufacturing function on the right-hand side will require upfront investment until product development and proprietary contract services get off the ground. However, they will grow into a big tree once they cross the break-even point. The company fully entered research peptide synthesis and antibody contract manufacturing services in December 2016. Peptides are molecules consisting of 2-50 residues of amino acids. In addition to custom-synthesising peptides with sequences that meet researchers’ requirements, the company is also developing a contract antibody production service using these peptides as materials (antigens).
Cosmo Bio’s business matrix
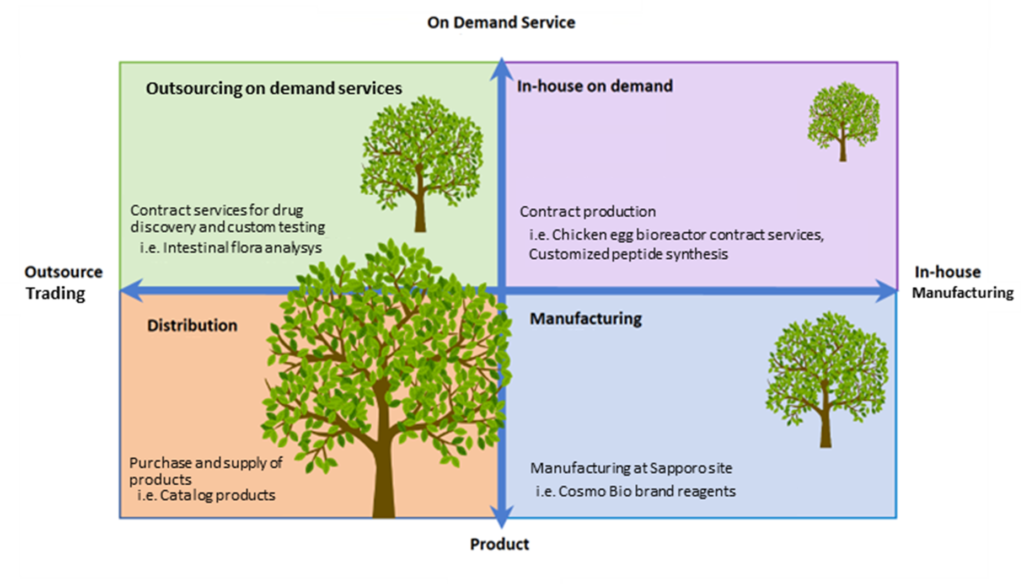
The chicken egg bioreactor is based on a technology that gene modified chickens modified by genome-editing technology to produce eggs with a value-added functional protein in the egg white, making it possible to produce the desired protein in large quantities at low cost for a long period. The company provides contract production services with the genome-edited chicken egg bioreactor technology.
On the other hand, custom peptide synthesis services are manufacturing services that go one step beyond research use reagent production and show an opportunity to support the provision of raw materials optimised for precision medicine. The company supplies research reagents, raw materials, customised bench tests, and customised material productions based on new technologies to support a broader range of life sciences.
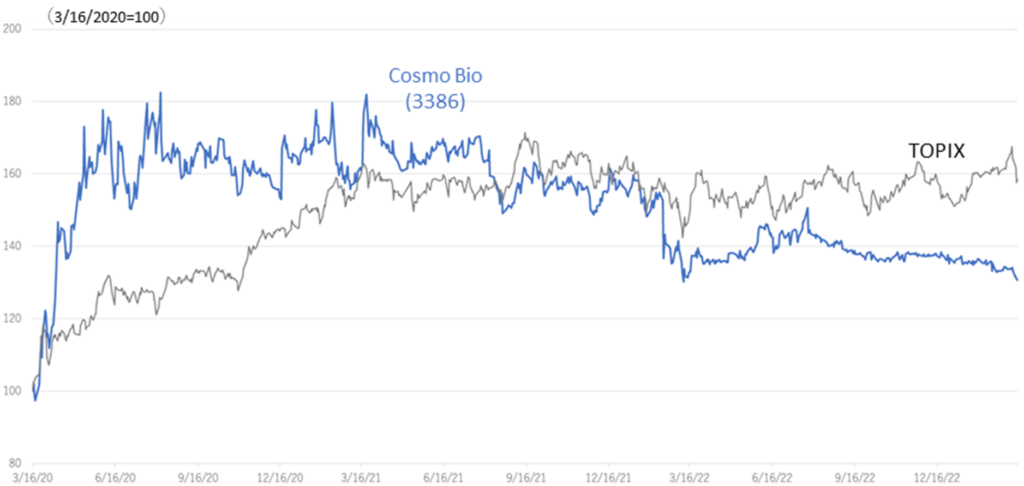
Share Price Trend
The company’s shares have traded in a box range of around 1,000 yen for the past year. The low trading volume is also a concern. The life science research reagent market is expected to grow steadily, and the company’s financial strength is solid and reassuring. However, inactive trading is thought to be due to difficulty finding growth drivers. Going forward, the share price may well be revalued as the company implements its new Three-Year Plan and progresses with new measures to increase earnings, including exports.
In its new Three-Year Plan, the company aims to create products and services that will become new pillars of growth by promoting the shift from trading to manufacturing function, as seen at the end of the previous chapter. The company also intends to expand into markets other than research use, and further developing overseas markets is an essential part of the company’s mission. It will take some more time for the company to show results in these new areas, but as earnings from these new businesses grow and the company’s earnings structure becomes more robust, the share price will likely be reassessed.
3386:5-year stock price move
Share price compared to TOPIX (last three years)
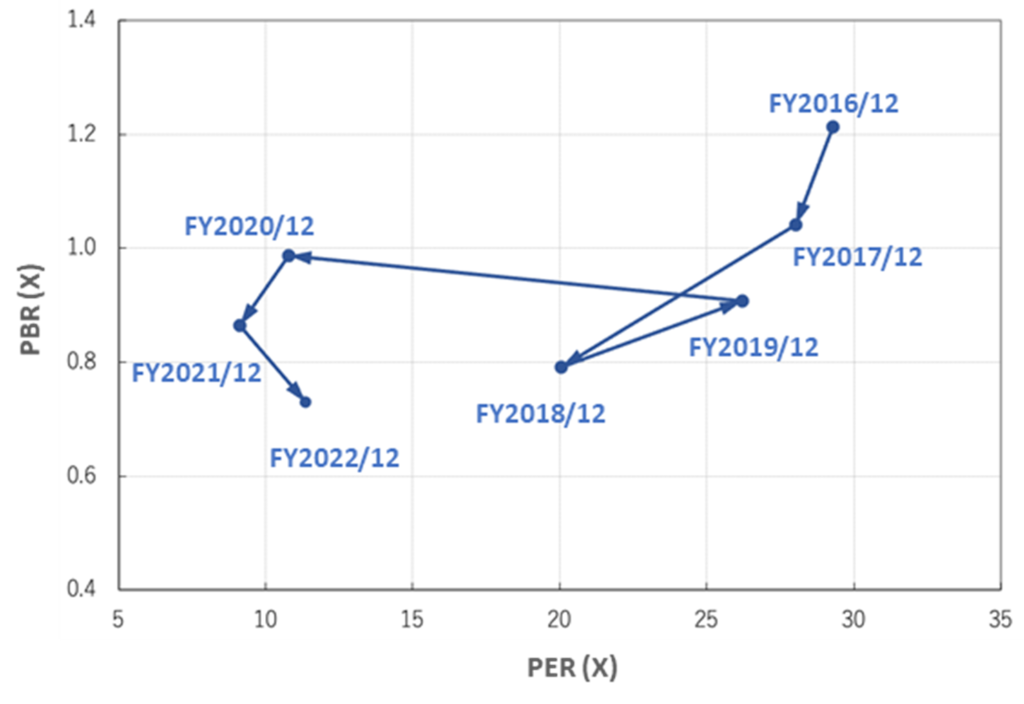
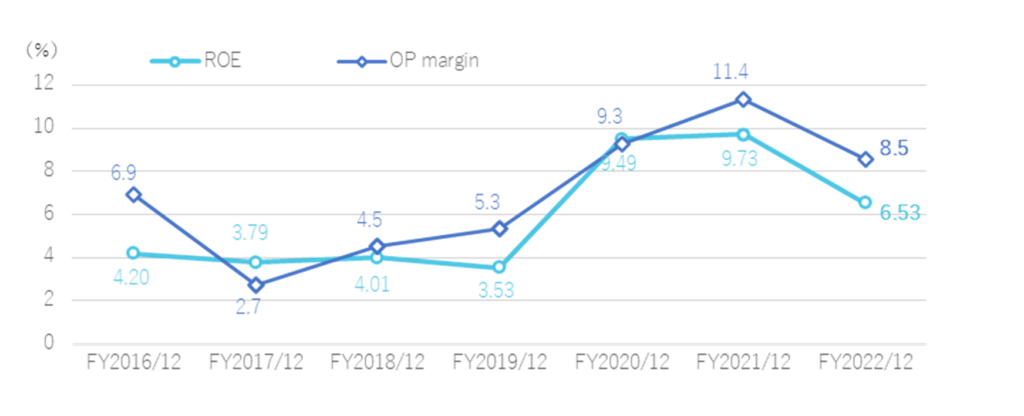
See the chart below for a discussion of share price valuations. In the recent past, PER and PBR have been well below the five-year average. In addition, the shares look undervalued compared to the trends over the past few years. Meanwhile, the company’s ROE and OP margins continue to improve and are around 10% in FY2020 and FY2021. The company’s profitability is seen as high for this type of business.
Historical PER/PBR (last five years)
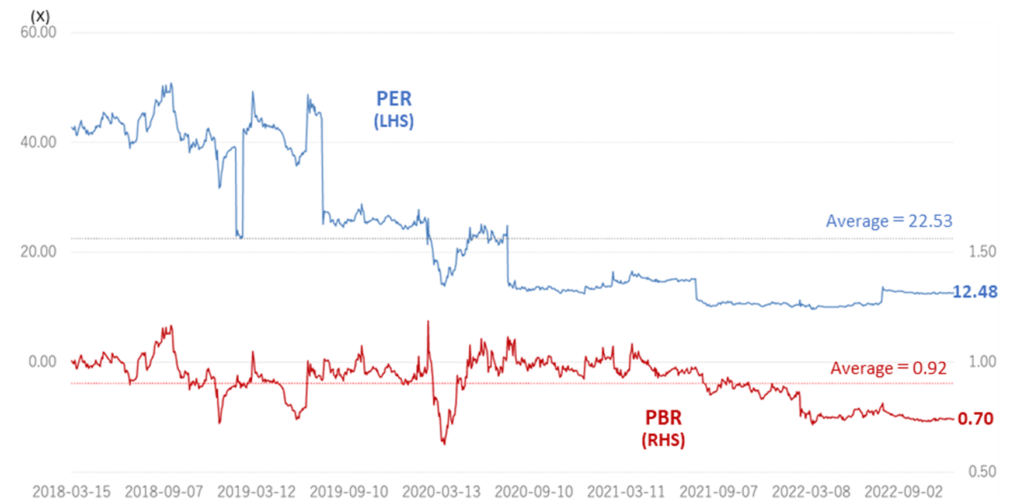
PER、PBR trend
ROE,Operating profit margin transition
Financial data
2012/12 |
2013/12 |
2014/12 |
2015/12 |
2016/12 |
2017/12 |
2018/12 |
2019/12 |
2020/12 |
2021/12 |
2022/12 |
|
[Statements of income] |
|||||||||||
Net sales |
7,241 |
7,050 |
7,235 |
7,357 |
7,427 |
7,068 |
7,261 |
7,590 |
8,092 |
9,231 |
9,553 |
Year-on-year basis |
0.7% |
-2.6% |
2.6% |
1.7% |
1.0% |
-4.8% |
2.7% |
4.5% |
6.6% |
14.1% |
3.5% |
Cost of sales |
4,057 |
4,429 |
4,811 |
4,976 |
4,655 |
4,535 |
4,602 |
4,710 |
4,940 |
5,572 |
6,112 |
Gross profit |
3,184 |
2,620 |
2,424 |
2,380 |
2,772 |
2,532 |
2,659 |
2,879 |
3,152 |
3,658 |
3,440 |
SG&A expenses |
2,386 |
2,349 |
2,261 |
2,180 |
2,257 |
2,339 |
2,330 |
2,474 |
2,399 |
2,609 |
2,624 |
Operating profit |
798 |
271 |
162 |
200 |
514 |
193 |
328 |
405 |
752 |
1,048 |
816 |
Year-on-year basis |
-10.4% |
-66.0% |
-40.2% |
23.5% |
157.0% |
-62.5% |
69.9% |
23.5% |
85.7% |
39.4% |
-22.1% |
Operating profit margin |
11.0% |
3.8% |
2.2% |
2.7% |
6.9% |
2.7% |
4.5% |
5.3% |
9.3% |
11.4% |
8.5% |
Non-operating profit |
46 |
177 |
128 |
175 |
21 |
208 |
89 |
72 |
71 |
71 |
57 |
Non-operating expenses |
43 |
3 |
5 |
2 |
51 |
3 |
13 |
7 |
6 |
20 |
83 |
Ordinary Profit |
801 |
444 |
285 |
373 |
483 |
397 |
403 |
470 |
817 |
1,099 |
790 |
Extraordinary profit |
3 |
9 |
46 |
34 |
55 |
8 |
|
|
190 |
|
|
Extraordinary expenses |
30 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
82 |
5 |
|
81 |
|
|
|
Income before income taxes |
774 |
451 |
330 |
407 |
456 |
400 |
403 |
388 |
1,008 |
1,099 |
790 |
Total income taxes |
336 |
137 |
131 |
158 |
180 |
148 |
126 |
142 |
307 |
331 |
238 |
Net profit |
411 |
313 |
201 |
230 |
254 |
237 |
260 |
237 |
674 |
737 |
517 |
Year-on-year basis |
-10.3% |
-23.8% |
-35.8% |
14.4% |
10.4% |
-6.7% |
9.7% |
-8.8% |
184.4% |
9.3% |
-29.9% |
Net profit ratio |
5.7% |
4.4% |
2.8% |
3.1% |
3.4% |
3.4% |
3.6% |
3.1% |
8.3% |
8.0% |
5.4% |
[Balance Sheets] |
|||||||||||
Current assets |
5,413 |
5,527 |
5,234 |
5,266 |
5,495 |
5,143 |
5,668 |
5,927 |
6,756 |
7,310 |
7,136 |
Cash equivalents and
|
2,143 |
2,036 |
1,482 |
1,498 |
1,948 |
1,483 |
2,268 |
2,516 |
3,259 |
3,555 |
3,036 |
Non-current assets |
1,541 |
2,750 |
2,927 |
2,523 |
2,438 |
2,982 |
2,832 |
2,962 |
2,883 |
2,761 |
3,176 |
Property, plant and equipment |
178 |
185 |
213 |
227 |
319 |
690 |
636 |
695 |
636 |
599 |
577 |
Investments and other assets |
1,201 |
2,456 |
2,613 |
2,071 |
1,842 |
2,041 |
1,943 |
2,068 |
2,081 |
1,979 |
2,428 |
Total assets |
6,955 |
8,277 |
8,161 |
7,790 |
7,934 |
8,126 |
8,501 |
8,890 |
9,640 |
10,072 |
10,313 |
Current liabilities |
916 |
818 |
1,130 |
1,017 |
916 |
799 |
945 |
987 |
1,226 |
1,093 |
1,038 |
Short-term borrowings |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
Non-current liabilities |
317 |
660 |
497 |
394 |
436 |
488 |
502 |
581 |
552 |
658 |
656 |
Total liabilities |
1,234 |
1,479 |
1,628 |
1,412 |
1,352 |
1,288 |
1,448 |
1,568 |
1,779 |
1,752 |
1,695 |
Total net assets |
5,720 |
6,797 |
6,532 |
6,378 |
6,581 |
6,838 |
7,053 |
7,321 |
7,861 |
8,319 |
8,617 |
Shareholders’ equity |
5,230 |
6,311 |
6,050 |
5,951 |
6,135 |
6,381 |
6,581 |
6,843 |
7,358 |
7,787 |
8,052 |
Share capital |
918 |
918 |
918 |
918 |
918 |
918 |
918 |
918 |
918 |
918 |
918 |
Capital surplus |
1,221 |
1,221 |
1,221 |
1,251 |
1,251 |
1,251 |
1,251 |
1,251 |
1,251 |
1,258 |
1,260 |
Retained earnings |
3,119 |
3,314 |
3,397 |
3,521 |
3,680 |
3,812 |
4,026 |
4,181 |
4,761 |
5,274 |
5,560 |
Treasury shares |
-67 |
-67 |
-67 |
-67 |
-67 |
-67 |
-67 |
-67 |
-67 |
-239 |
-216 |
Valuation/exchange differences |
37 |
924 |
579 |
327 |
352 |
466 |
451 |
558 |
494 |
574 |
530 |
Total liabilities and net assets |
6,955 |
8,277 |
8,161 |
7,790 |
7,934 |
8,126 |
8,501 |
8,890 |
9,640 |
10,072 |
10,313 |
(Shareholders’ equity ratio) |
75.2% |
76.2% |
74.1% |
76.4% |
77.3% |
78.5% |
77.4% |
77.0% |
76.3% |
77.3% |
78.1% |
[Statements of cash flows] |
|||||||||||
Cash flow from operating activities |
347 |
126 |
297 |
129 |
573 |
89 |
908 |
549 |
803 |
648 |
284 |
Cash flow from investing activities |
-167 |
-99 |
-227 |
-263 |
99 |
-235 |
-185 |
-115 |
42 |
-145 |
-291 |
Cash flow from financing activities |
-126 |
-126 |
-122 |
-151 |
-107 |
-109 |
-85 |
-85 |
-97 |
-420 |
-236 |
Net increase in cash and cash equiv. |
61 |
-97 |
-52 |
-285 |
549 |
-264 |
684 |
348 |
743 |
95 |
-218 |
Cash and cash equiv. at
|
1,471 |
1,532 |
1,435 |
1,383 |
1,098 |
1,648 |
1,383 |
2,068 |
2,416 |
3,159 |
3,255 |
Cash and cash equiv. at end of period |
1,532 |
1,435 |
1,383 |
1,098 |
1,648 |
1,383 |
2,068 |
2,416 |
3,159 |
3,255 |
3,036 |
Free cash flow |
180 |
27 |
70 |
-134 |
672 |
-146 |
723 |
434 |
845 |
503 |
-7 |
Company data
Company Profile
Sales by product category
Cosmo Bio Co., Ltd.
【Head Office】
9F Toyo-Ekimae Bldg., 2-20, Toyo 2-chome
Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-0016
【Sapporo Office】
3-513-2, Zenibako, Otaru City, Hokkaido
【Shinsuna logistics centre】
12-39, Shinsuna, Koto-ku, Tokyo
3F, Building B, Warehouse No. 3, Shinsuna, Nippon Express Co.
Number of Employees :146 (Consolidated)
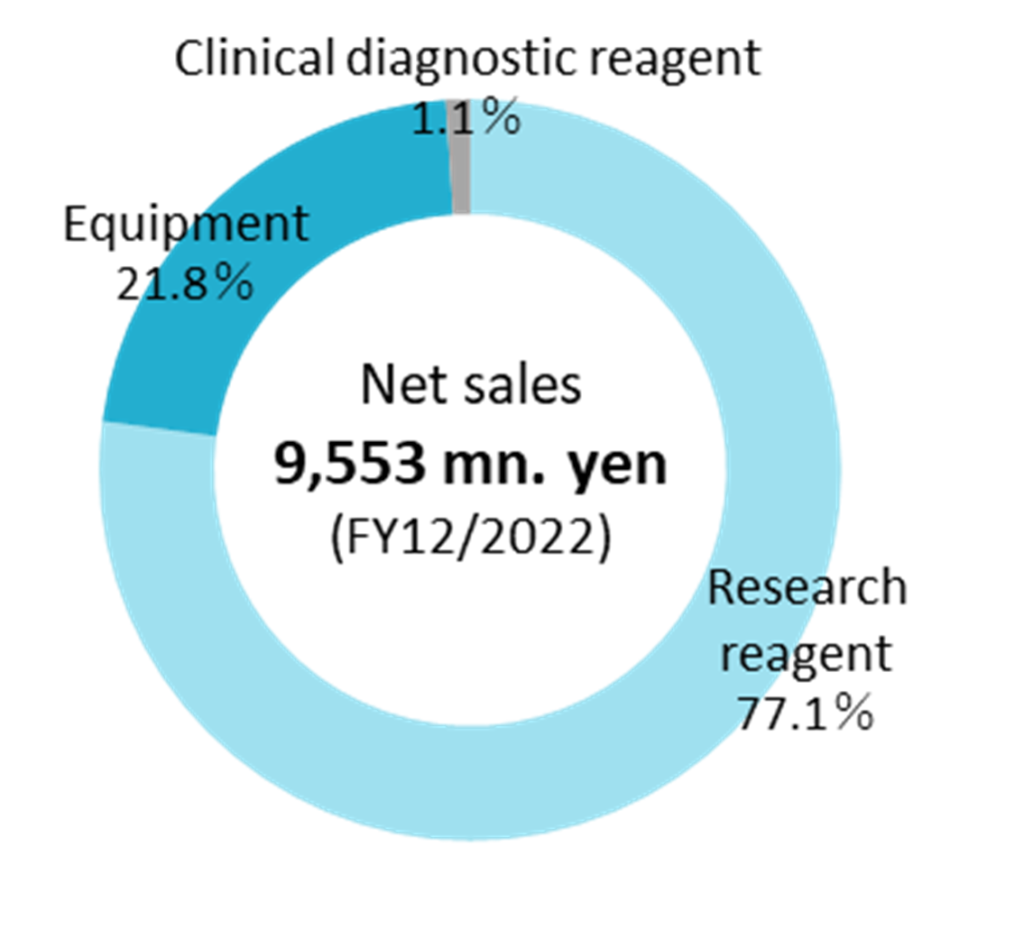
History
| Month/Year | Event |
|---|---|
| Aug. 1983 | Maruzen Oil Biochemicals Co. Ltd. was established as a subsidiary of Maruzen Oil (now Cosmo Oil Co., Ltd.) in Minato-ku, Tokyo, for the purpose of marketing basic biotechnology research reagents. |
| Apr. 1986 | Company name changed to Cosmo Bio Ltd. and sales of bio-research equipment begun. |
| Dec. 1986 | Licensed to sell medicines |
| Apr. 1998 | Establishment of wholly-owned subsidiary CB Development Co., Ltd. to search for suppliers. |
| Sep. 2000 | Independence from Cosmo Oil through a management buyout (MBO). CB Development Co., Ltd. became a non-subsidiary company through a share transfer. |
| Dec. 2000 | Absorption merger of CB Development Co., Ltd. |
| Aug. 2004 | Establishment of wholly-owned subsidiary Cosmo Bio USA Inc. in San Diego, California, USA, to search for suppliers and promote exports. |
| Sep. 2005 | Listed on the JASDAQ stock exchange. |
| Dec. 2006 | Acquired 80% of the shares of Primary Cell Co., Ltd., a company engaged in the research, development, manufacture and sale of primary cultured cells (primary cells) and contract analysis using these cells, and made it a subsidiary. |
| Nov. 2007 | Acquired 30% of the outstanding shares of BM Equipment Co., Ltd., an importer and distributor of consumables and equipment for bio-research, and made it an equity-accounted affiliate. |
| Jul. 2008 | Primary Cell Co., Ltd., a consolidated subsidiary, became a wholly owned subsidiary. |
| Mar. 2010 | Acquired an additional 33% of the outstanding shares of BM Equipment Co., Ltd., making it a consolidated subsidiary with a total shareholding of approximately 63%. |
| Jan. 2013 | Relocated the distribution centre and started operation at the Shinsuna Logistics Centre. |
| Jul. 2013 | Merged with Primary Cell Co., Ltd. |
| Jul. 2013 | Listed on the JASDAQ (Standard) of the Tokyo Stock Exchange following the merger of the Tokyo Stock Exchange and the Osaka Securities Exchange. |
| Nov. 2016 | Established a joint venture Proteintech Japan Co., Ltd. with Proteintech Group, Inc. |
| Oct. 2017 | Relocated and consolidated Sapporo business facilities and opened the Sapporo Site. |
| Jan. 2018 | Cosmo Bio USA, became a consolidated subsidiary. |
| Mar. 2022 | Transition to a company with an audit committee |
| Apr. 2022 | Listed on the TSE Standard following the reorganisation of the Tokyo Stock Exchange. |
Top management
President:Haruhisa Sakurai

Feb. 1990 Joined Maruzen Petrochemical Co., Ltd.
Sep. 1990 Head of Biotechnology Laboratory, Maruzen Petrochemical Co., Ltd.
Oct. 2000 Joined the Company
Mar. 2006 Director and Head of Product Communications Department
Mar. 2011 President and Representative Director, Cosmo Bio USA, Inc.
Mar. 2012 Managing director and Head of Product Communications Department and Advanced Sales Department
Mar. 2014 Senior Managing Director and Head of Technical Service Department
Mar. 2016 President and Representative Director (to present)
Nov. 2016 President and Representative Director, Proteintech Japan Co., Ltd.
Mar. 2017 President and Representative Director, BM Equipment Co., Ltd.
Mar. 2022 Chairman and Director, Cosmo Bio USA, Inc. (to present)
Senior Managing Director : Norihiko Shibayama
Apr. 1994 Joined Maruzen Petrochemical Co., Ltd.
Oct. 2000 Joined the Company
Apr. 2012 General Manager, Information Systems Department
Mar. 2014 Director, BM Equipment Co., Ltd.
Nov. 2016 General Manager of General Affairs Department and General Manager of the Information Systems Department
Mar. 2017 Director and General Manager of the General Affairs Department and Information Systems Department
Mar. 2020 Managing Director and General Manager of the General Affairs Department and Information Systems Department
Director and General Manager of General Affairs Department, BM Equipment Co., Ltd.
Mar. 2022 President and Representative Director of BM Equipment Co., Ltd. (to present)
Apr. 2022 Managing Director and General Manager of the General Affairs Department
Mar. 2023 Senior Managing Director and General Manager of the General Affairs Department (to present)
Managing Director : Junko Tochigi
Apr. 1998 Joined the Company
Apr. 2013 Head of Product Communications Department
Mar. 2017 Director and Head of Product Communications Department
Apr. 2017 Director and Head of Corporate Planning Department
Mar. 2021 Director, BM Equipment Co., Ltd (to present)
Mar. 2022 President and Representative Director, Cosmo Bio USA, Inc. Representative Director, Proteintech Japan Co., Ltd. (to present)
Mar. 2023 Managing director and Head of Corporate Planning Department (to present)
Director : Masanori Hayashi
Apr. 1994 Joined Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co., Ltd.
May. 2012 Joined the Company
Apr. 2019 Head of Finance Department
Mar. 2022 General Manager, Finance Department, BM Equipment Co., Ltd (to present)
Mar. 2023 Director and Head of Finance Department (to present)
Director, Full-time Audit and Supervisory Committee:Kazutoshi Sato
Apr. 1987 Joined Sumitomo Real Estate Sales Co., Ltd.
Jan. 1993 Joined Cosmo Oil Co., Ltd.
Jun. 2011 Branch Manager, Sapporo Branch, Cosmo Oil Co., Ltd.
Jun. 2014 Branch Manager, Takamatsu Branch, Cosmo Oil Co., Ltd.
Oct. 2015 Cosmo Oil Marketing (Japan) Co., Ltd., Takamatsu Branch Branch manager
Jun. 2017 Director, Executive Officer and General Manager, General Affairs Department, Maruzen Petrochemical Co., Ltd.
Mar. 2020 Outside auditor of the company Auditor of BM Equipment Co., Ltd. (present post)Mar. 2022 Director and full-time audit committee member (to present)
Director, Audit and Supervisory Committee Member:Haruo Sasaki
Nov. 1974 Joined Chuo Audit Corporation
Feb. 1990 Established Sasaki Accounting Office, Director (to present)
Dec. 2000 Outside auditor of the Company
Mar. 2022 Director and Audit Committee member (to present)
Nov. 1974 Joined Chuo Audit Corporation
Feb. 1990 Established Sasaki Accounting Office, Director (to present)
Dec. 2000 Outside auditor of the CompanyMar. 2022 Director and Audit Committee member (to present)
Director, Audit and Supervisory Committee Member:Katsutoshi Fukami
Apr. 1973 Joined Tokyo Small and Medium Business Investment & Consultation Co., Ltd.
Jun. 2004 Director, Tokyo Small and Medium Business Investment & Consultation Co., Ltd.
Jun. 2007 Managing Director, Tokyo Small and Medium Business Investment & Consultation Co., Ltd.
Jun. 2013 Auditor, Tokyo Small and Medium Business Investment & Consultation Co., Ltd. (to present)
Mar. 2014 Outside auditor of the Company
Mar. 2022 Director and Audit Committee member (to present)
Director, Audit and Supervisory Committee Member:Kazuya Shimamura
Oct. 1995 Joined Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu (now Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu LLC)
Apr. 1998 Registered as a chartered accountant
Oct. 2004 Registered as a lawyer Joined Abe, Ikubo & Katayama Law Office
Mar. 2008 Established Shimamura Law & Accounting Office,Representative (to present)
Mar. 2014 Outside director of the Company
Mar. 2022 Director and Audit Committee member (to present)
Skills matrix of the Board of Directors’ Members
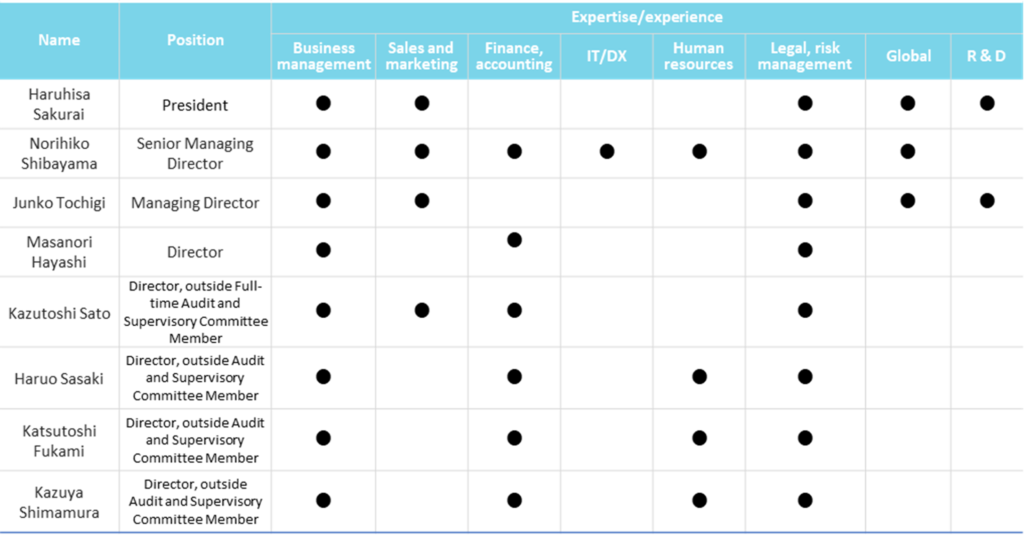
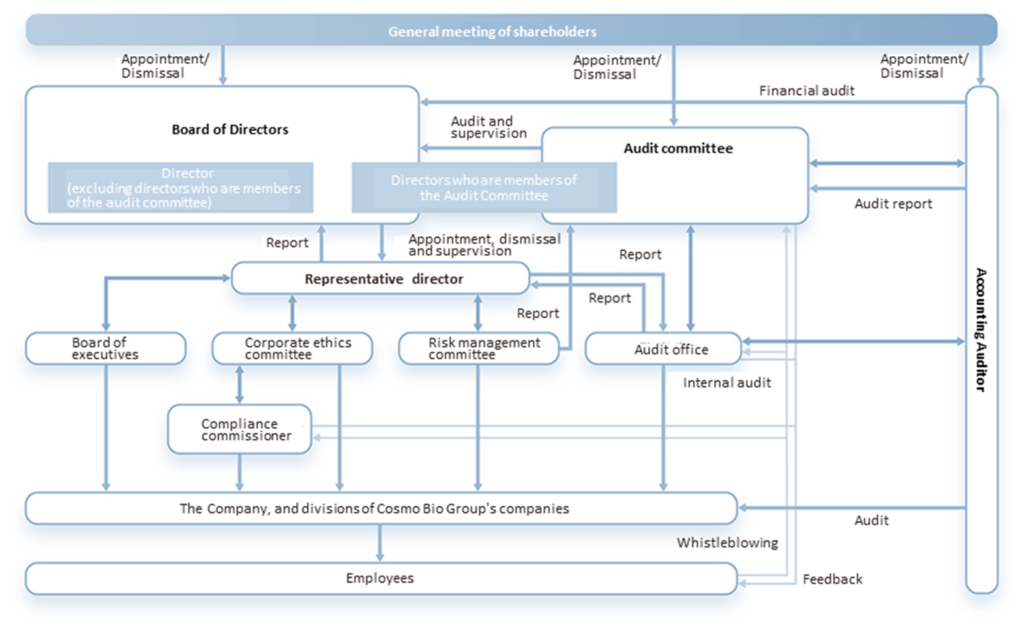
The company transitioned to a company with an audit committee in March 2022. The board of directors currently consists of one representative director, one senior managing director, one managing director and five directors. Four of the five directors are members of the audit committee and outside directors. All eight directors are Japanese, of which one is female.
Corporate governance structure
Major shareholders
| Name | Number of shares owned |
Ratio of the number of shares owned to the total number of issued shares (%) |
| Tokyo Small and Medium Business Investment & Consultation Co., Ltd. |
1,152,000 | 19.83 |
| Mizuho Trust & Banking Corporation Cosmo Oil Co., Ltd. Pension Fund. Re-trustee Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd. |
576,000 | 9.92 |
| Hikari Tsushin, Inc. | 382,000 | 6.58 |
| Cosmo Bio Employee Stock Ownership Plan | 122,900 | 2.12 |
| Harada, Katsuyuki | 121,400 | 2.09 |
| Yakult Honsha Company, Ltd. | 100,400 | 1.73 |
| Yumiko Suzuki | 82,300 | 1.42 |
| Toshiaki Funato | 75,400 | 1.30 |
| Shoichi Matsunami | 74,300 | 1.28 |
| Harada, Masanori | 69,500 | 1.20 |
| Total | 2,756,200 | 47.47 |
Note: The percentage of shares held to the total number of shares issued (%) excludes treasury shares (234,676 shares).
Source: Omega Investment from company materials
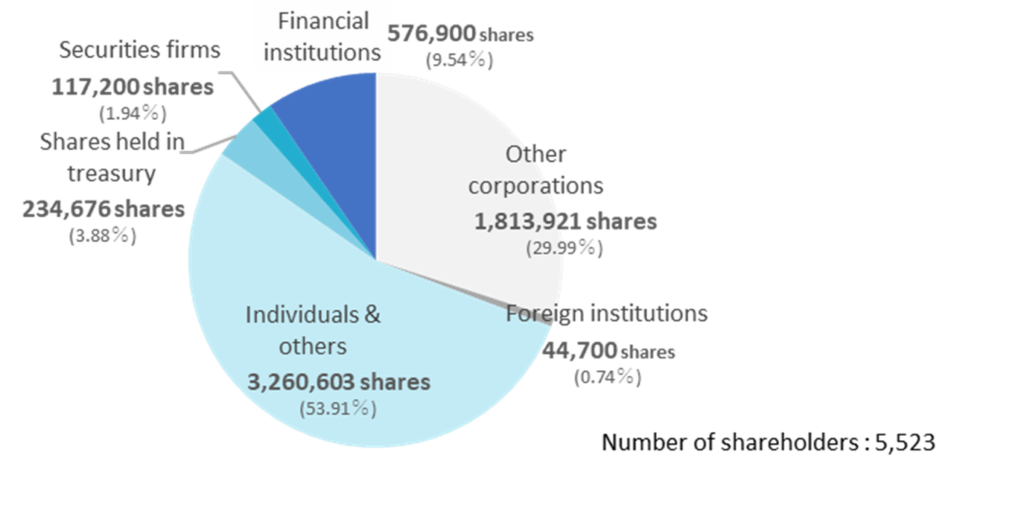
Shareholding by ownership (As of 31, December, 2022)
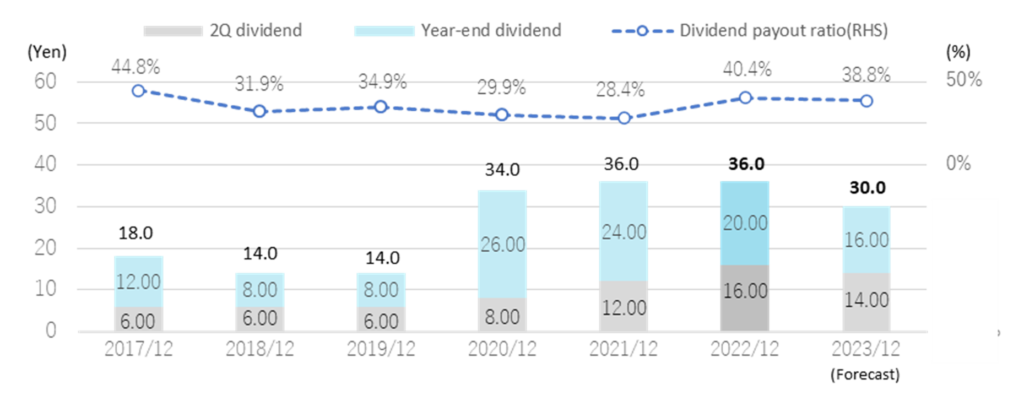
Shareholder return policy
Dividends